- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 29 Downloads
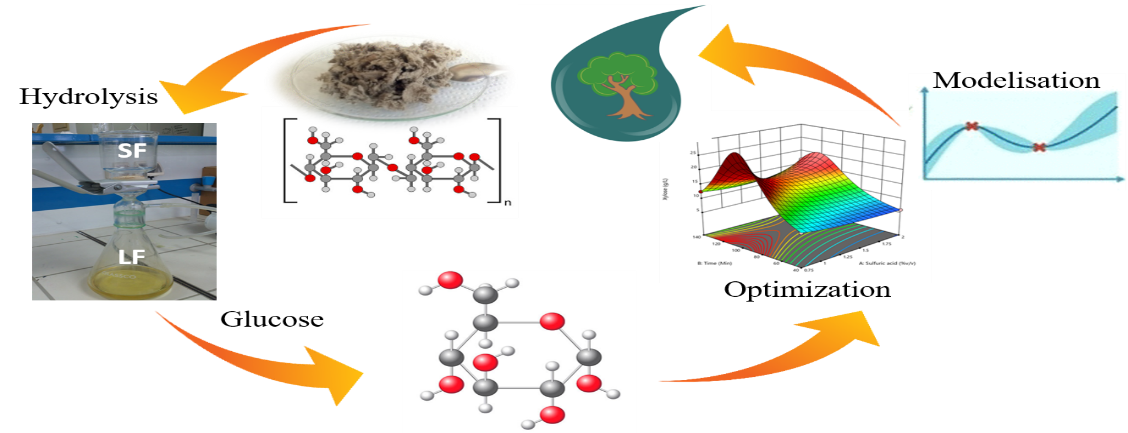
In papermaking industry, large water consumption and hazardous wastes generation, particularly paper sludge, present environmental challenges. This study focuses on the valorization of the paper sludge by optimizing the extraction of total sugars through chemical treatment under various operating conditions. A central composite design was used to investigate treatment conditions, by varying chemical treatment agent (sulfuric acid, H2SO4, phosphoric acid, H3PO4, sodium hydroxide, NaOH, and hydrogen peroxide, H2O2), agent concentration (0.75%, 1.5%, and 2%) and treatment duration (up to 140 minutes). Additionally, experiments were conducted to assess biogas production, with monitoring of key parameters such as cumulative biogas volume, chemical oxygen demand (COD) and total sugar. Results were analyzed using the modified Seaman model to elucidate chemical treatment reaction mechanisms. Optimal conditions, achieved with 2% (v/v) sulfuric acid treatment at 100°C for 120 minutes, yielded a maximum total sugar concentration of 1738.96 mg/L. These findings demonstrate the potential for efficient utilization of paper sludge for bioconversion into biogas, contributing to sustainable waste management and resource recovery.