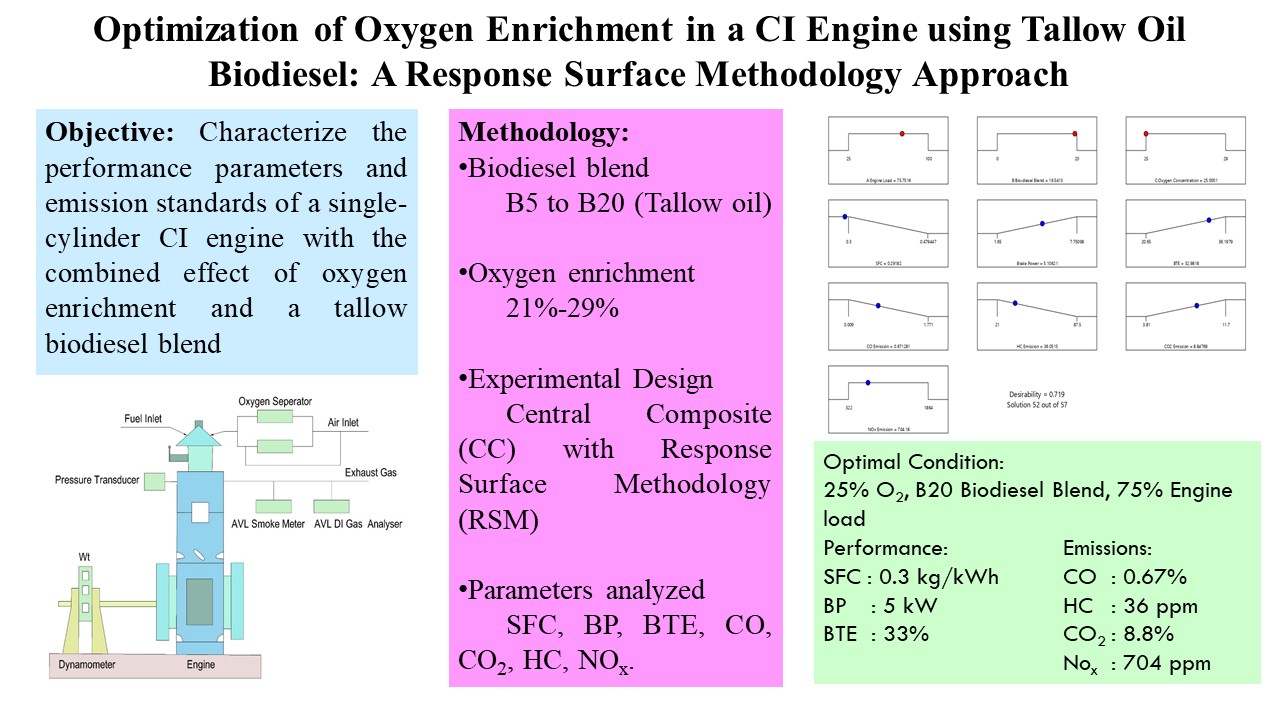
The growing need for sustainable energy solutions has driven significant interest in biodiesel as a suitable replacement for fossil fuels. This research aims to characterize the performance parameters and emission standards of a single-cylinder CI engine with the combined effect of oxygen enrichment and a biodiesel blend. Tallow oil derived from animal fats is used as biodiesel because of its renewable properties, cost-effectiveness, and green energy applications. The response surface methodology (RSM) optimizes engine parameters for enhanced efficiency and reduced emissions. Oxygen enrichment is done at various oxygen concentrations of 21-29%, and the tallow oil biodiesel blend of B5 to B20 is used. The central composite (CC) design was used to design experimentation and enable the development of regression models that predict engine responses. Performance factors such as specific fuel consumption (SFC), brake power (BP), brake thermal efficiency (BTE), and emission characteristics such as carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), hydrocarbon (HC), and nitrogen oxides (NOx) are the factors analyzed. The analysis found that 25% oxygen enrichment with a B20 biodiesel blend and a 75% engine load condition provides a desirability of 0.719, and the desirable parameters obtained are 0.3 kg/kWh of SFC, brake power of 5 kW, and the brake thermal Efficiency as 33%. When we come to emissions, it is found that the CO emission of 0.67%, the HC emission of 36 ppm, the CO2 emission of 8.8%, and the NOx emission of 704 ppm. This result shows the optimum condition for the operation of the diesel engine.
Total file downloads: 15