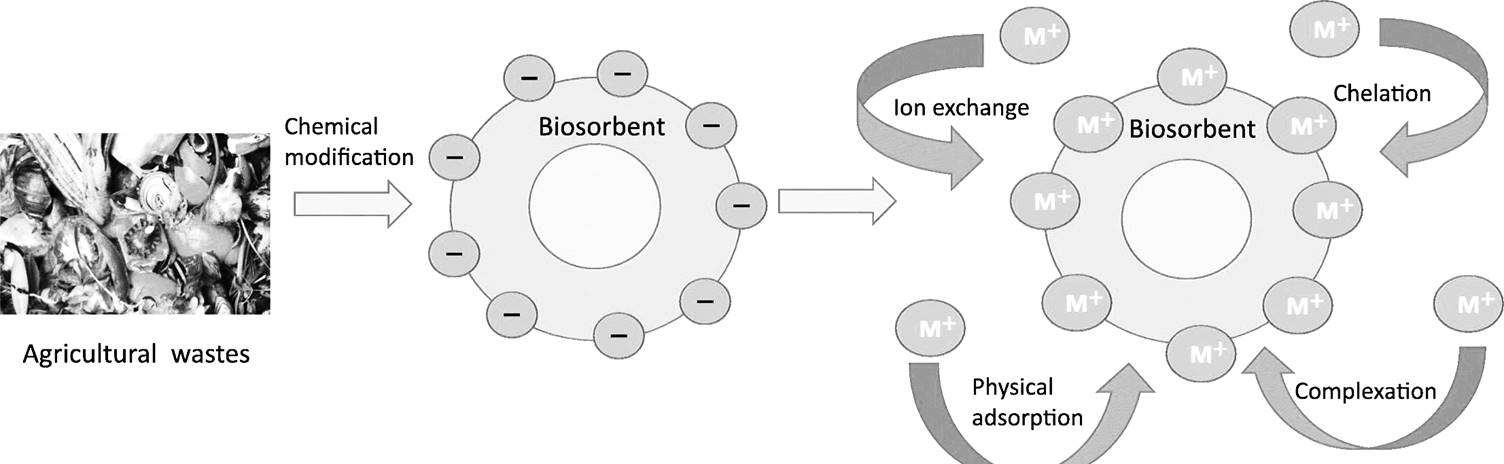
This study used a biosorbent, derived from processed Prosopis juliflora root powder to treat wastewater and remove lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), and copper (Cu) ions. The biosorption process was influenced by factors including temperature (25 to 65°C), biomass content (1 to 5 g), pH levels (1.0 to 7.0), and adsorbate concentration (10 to 50 mg/L). The absorption of lead and copper ions was investigated using batch sorption methods. The outcomes exhibited the maximum efficiency of adsorption achieved at a pH of 4.0, with the removal efficiencies of 94.92% for lead (Pb), 89.73% for cadmium (Cd), and 90.28% for copper (Cu). Even though the pseudo-first and second-order kinetics were considered, the experimental results aligned with the Freundlich isotherm model. Furthermore, the thermodynamic constants (ΔG°, ΔH°, and ΔS°) indicated that the Pb, Cd, and Cu metal ions adsorption using Prosopis juliflora root powder was feasible under the experimental conditions.
Total file downloads: 58