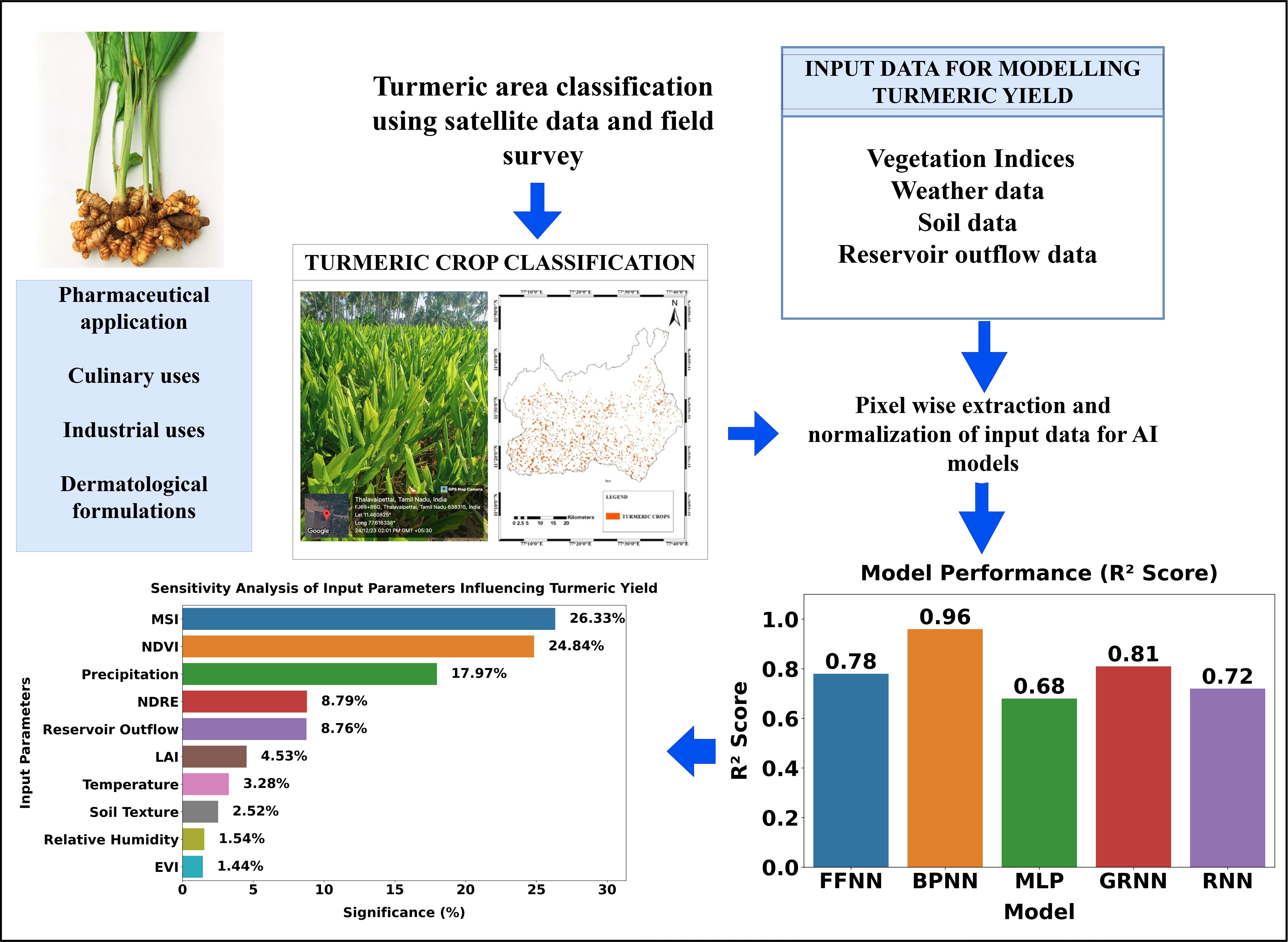
Crop yield forecasting is an essential element for farm management directly impacting food security, economic planning and sustainability of resources. This study integrated remote sensing data and machine learning approaches to develop an advanced turmeric yield modelling framework for turmeric crops grown in the study area. The input parameters included vegetation indices, soil texture and meteorological and hydrological variables. The findings showed that the Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN) model (R2 = 0.96) outperformed other models utilized in this study in predicting turmeric yield. Sensitivity analysis further highlighted that the turmeric yield was highly sensitive to the Normalized Difference Vegetation Index) NDVI, Moisture Stress Index (MSI) and precipitation. This modelling approach provided a reliable tool for early yield estimation at the maturity phase with a 0.86 % deviation from the actual turmeric yield, aiding farmers and policymakers in optimising crop management practices and enhancing decision-making processes. This study presented a holistic approach for scalable data-driven agricultural innovation contributing to efficient and sustainable crop production systems.
Total file downloads: 20