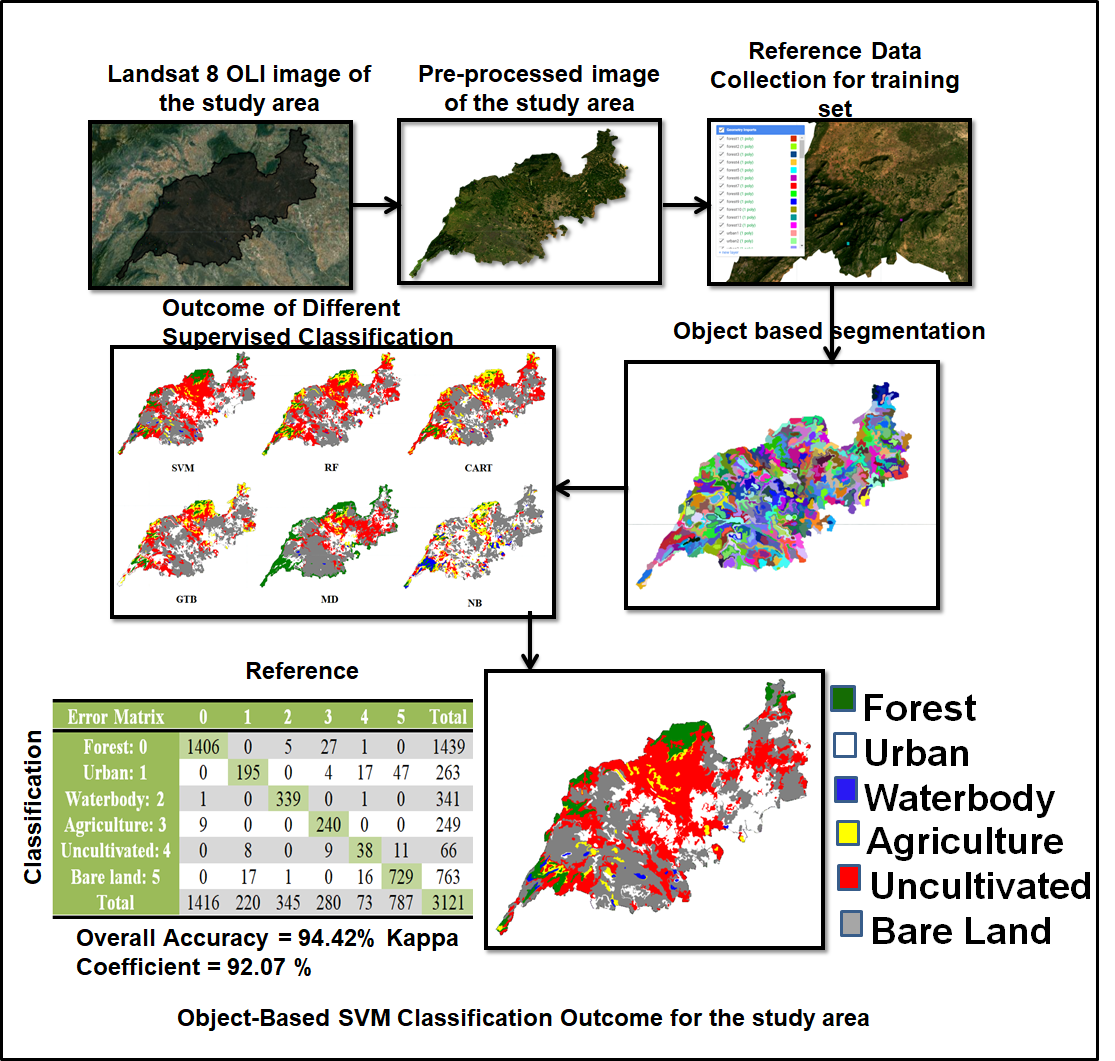
Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) maps perform a significant part in Remote Sensing (RS) in monitoring and analyzing earth information for human development. Because of the high spectrum variability, LULC classification from RS data is extremely difficult. The study's objective is to assess the object-based LULC classification (OBC) accuracy of composite images from the Landsat 8 OLI (Operational Land Imager) and auxiliary features using SNIC segmentation and five classifiers on Google Earth Engine (GEE). The outcome of the study indicates that the OBC with only spectral features achieves lesser accuracy because small objects on the land surface cannot be observed. But when OBC is paired with a variety of auxiliary features, the OBC may recognize small objects with greater accuracy. After many subsequent assessments the combination of the following aspect: composite image of all the seven bands, new feature set, Simple Non-Iterative Clustering (SNIC) segmentation algorithm, and Support Vector Machine (SVM) classification algorithm gives better accuracy of ~ 94.42% and kappa coefficient of 92.07. The inclusion of auxiliary features and the OBC method reduces the misclassification rate related to the confusion of bare land, uncultivated land, and urban, which provides accurate information on forest, waterbody, and bare land classes.
Total file downloads: 28