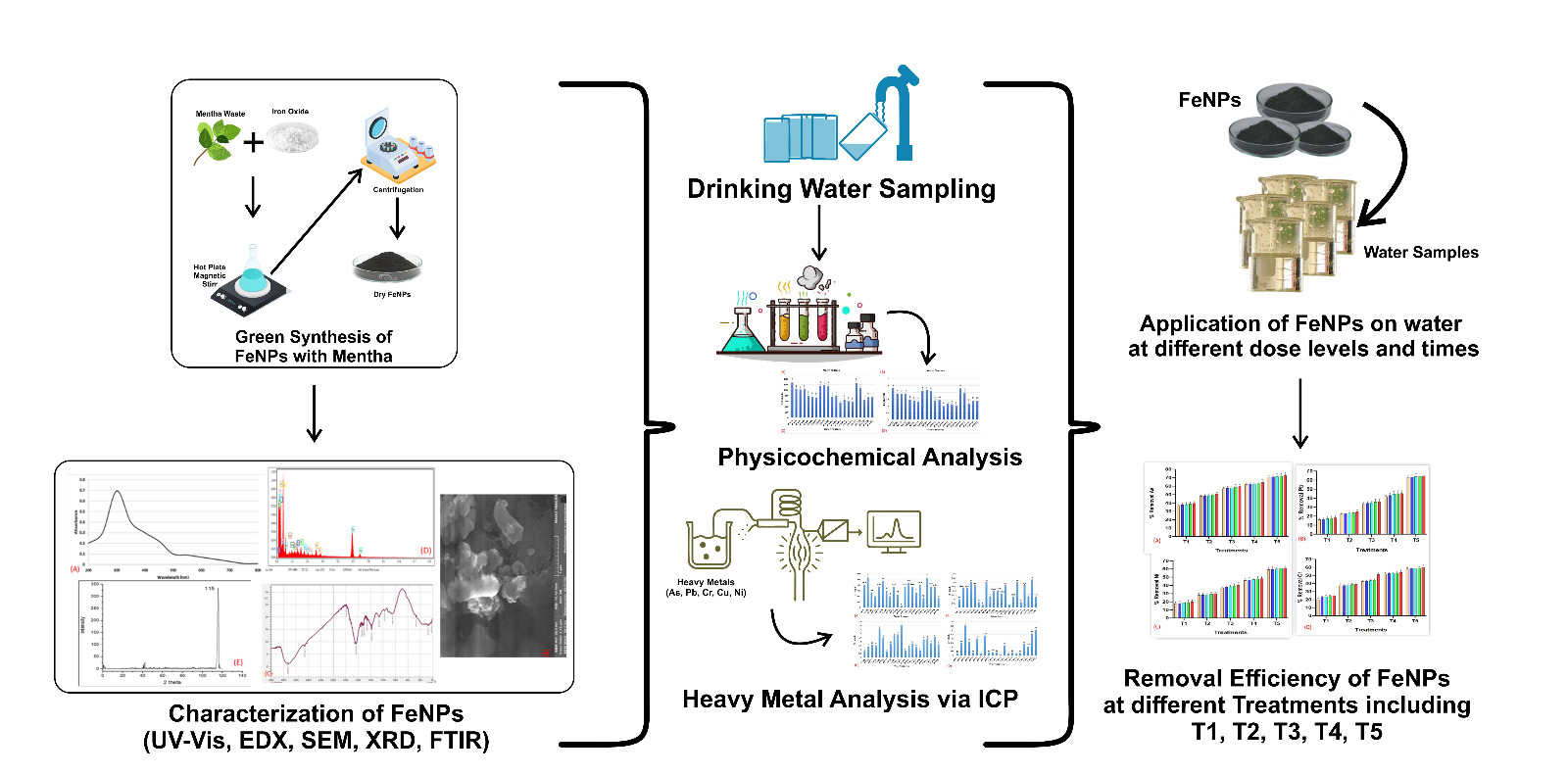
The present study was conducted to examine the synthesis and utilization of mentha-mediated iron nanoparticles as an innovative adsorbent to remove heavy metals from water. Iron nanoparticles were synthesized by employing mentha extract as a reducing and stabilizing agent. The synthesized FeNPs were characterized by SEM for morphology, , ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy for optical properties (UV), and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR for functional groups, EDX for elemental composition, and XRD for structure and composition.. The SEM images showed the defined nanoparticles exhibiting a consistent size distribution. The FTIR and UV analyses validated the effective formation of nanoparticles and identified functional groups that participated in the reduction process. Subsequently, synthesized nanoparticles were implemented as adsorbents to remove extract particular heavy metals from water at varying doses and times. The investigation of experimental samples was carried out by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES) to measure the heavy metal concentrations in the water. The findings of the study indicated that iron nanoparticles mediated by Mentha were effective for removing concentration of heavy metals more than 60% of all the selected heavy metals in the water samples. This study contributes to the dynamic domain of water purification strategies propelled by nanotechnology. It highlights the potential of utilizing natural extracts, such as Mentha, in environmentally friendly synthesis processes to remediate environmental issues. The results have potential implications for the advancement of environmentally friendly and efficient strategies to tackle the issue of water pollution.
Total file downloads: 8