- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 39 Downloads
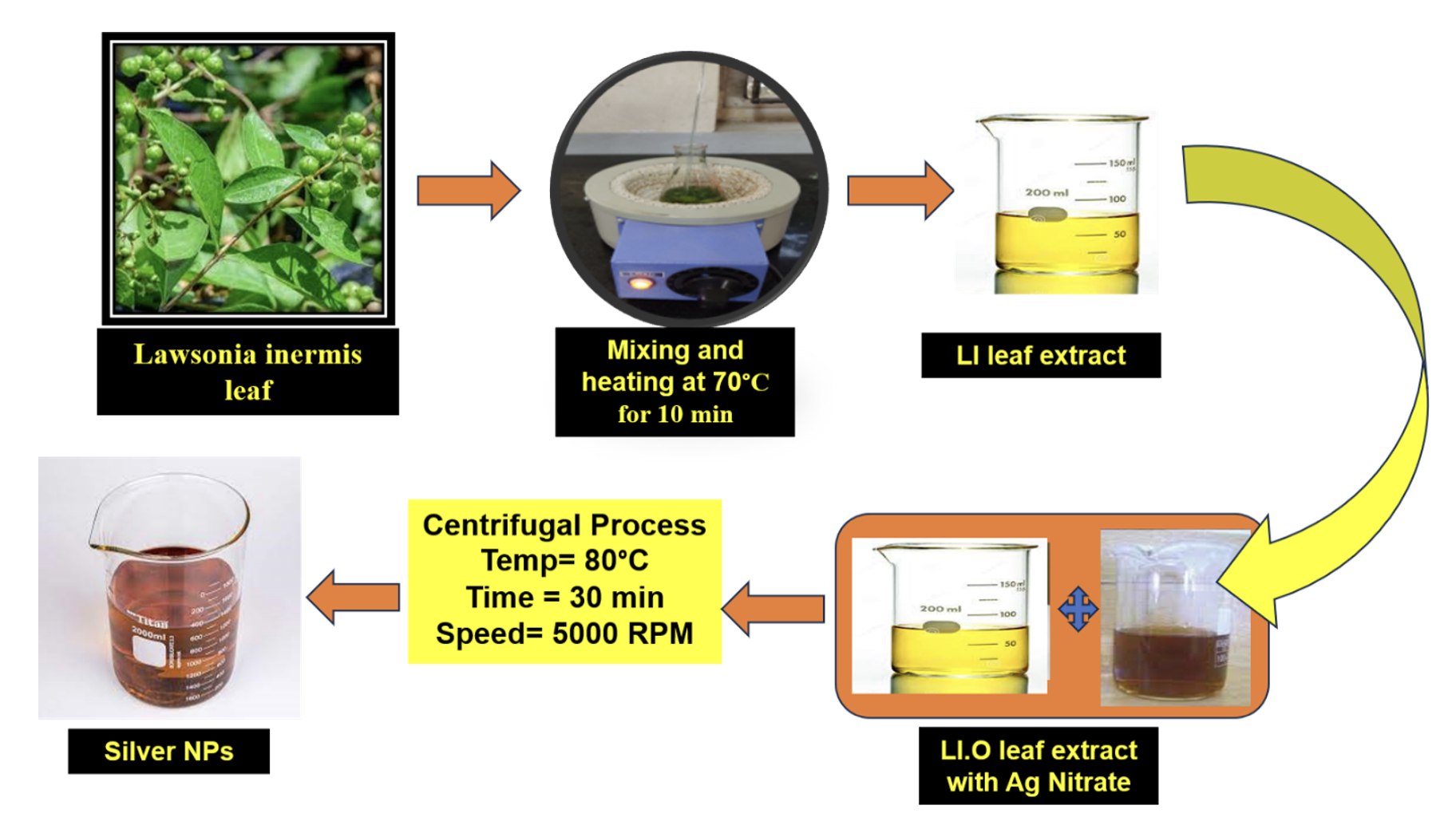
In response to the growing demand for eco-friendly and efficient catalysts in wastewater treatment, this study introduces a novel, biosynthesized silver nanoparticle (AgNP) using leaf extract from Lawsonia inermis, a widely available plant. We employed a unique concentration mixture of 0.015 mg/mL leaf extract and 2.0 mM silver nitrate to achieve optimal results under atmospheric conditions. Comprehensive characterization was conducted through X-ray diffraction, transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and ultraviolet-visible absorption spectroscopy. Remarkably, these Lawsonia inermis-synthesized AgNPs (LI-AgNPs) demonstrated superior catalytic degradation of organic pollutants, such as 4-nitrophenol, methylene blue, eosin yellow, and methyl orange. Among them, 4-nitrophenol was reduced most efficiently, following pseudo-first order kinetics. The LI-AgNPs exhibited unprecedented catalytic potential, evidenced by a sharp decline in methyl orange absorption and the emergence of a new hydrazine compound signal at 280 nm. With a catalytic loading as low as 0.2 mg/mL, we achieved an astounding 82.5% dye removal. This innovative approach advances the field of environmental remediation