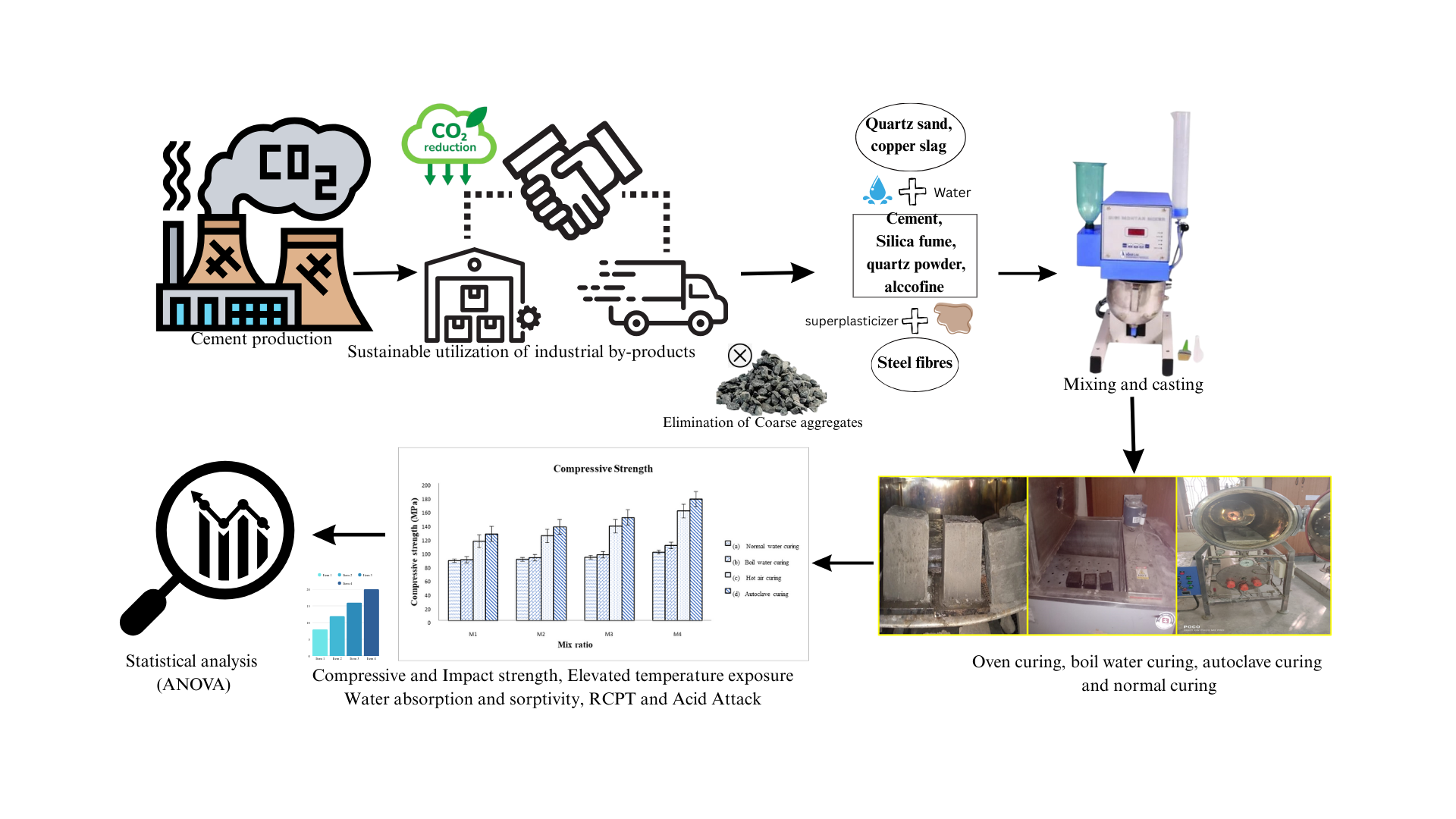
Cement production significantly contributes to global carbon dioxide emissions; in Reactive Powder Concrete (RPC), incorporation of sustainable by-products and elimination of coarse aggregate reduces emission, improves particle packing, and enhances strength, echoing the shift from normal concrete to Ultra-High-Performance Concrete (UHPC). Among them, foremost is RPC, which is made of fine particles such as quartz sand, quartz powder, and cementitious materials such as silica fume, cement, admixtures, and fibres, which improves ductility. This research investigates the mechanical properties like compressive strength and impact strength and durability properties like water absorption, water sorptivity, acid attack, chloride penetration, and residual compressive strength under elevated temperatures of 300 °C, 600 °C, and 900 °C. This paper also examines the effectiveness of various curing conditions and adding cementitious materials to enhance RPC. The various curing conditions taken for the study are water curing, boil water curing, autoclave curing, and oven curing. The test results show a compressive strength of 176.5±0.62 MPa was achieved in RPC by replacing 10 % cement with Alccofine and 40 % quartz sand with copper slag under autoclave curing. Also, the significant effect of mix ratios and curing conditions on the strength of concrete is done by ANOVA analysis. The results suggest that the mixes with high cement and pozzolonic content under the autoclave curing method yield the strongest material. This research aligns with sustainable goals such as SDG 9: Industry, Innovation, and Infrastructure; SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities; and SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production.
Total file downloads: 21