- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 10 Downloads
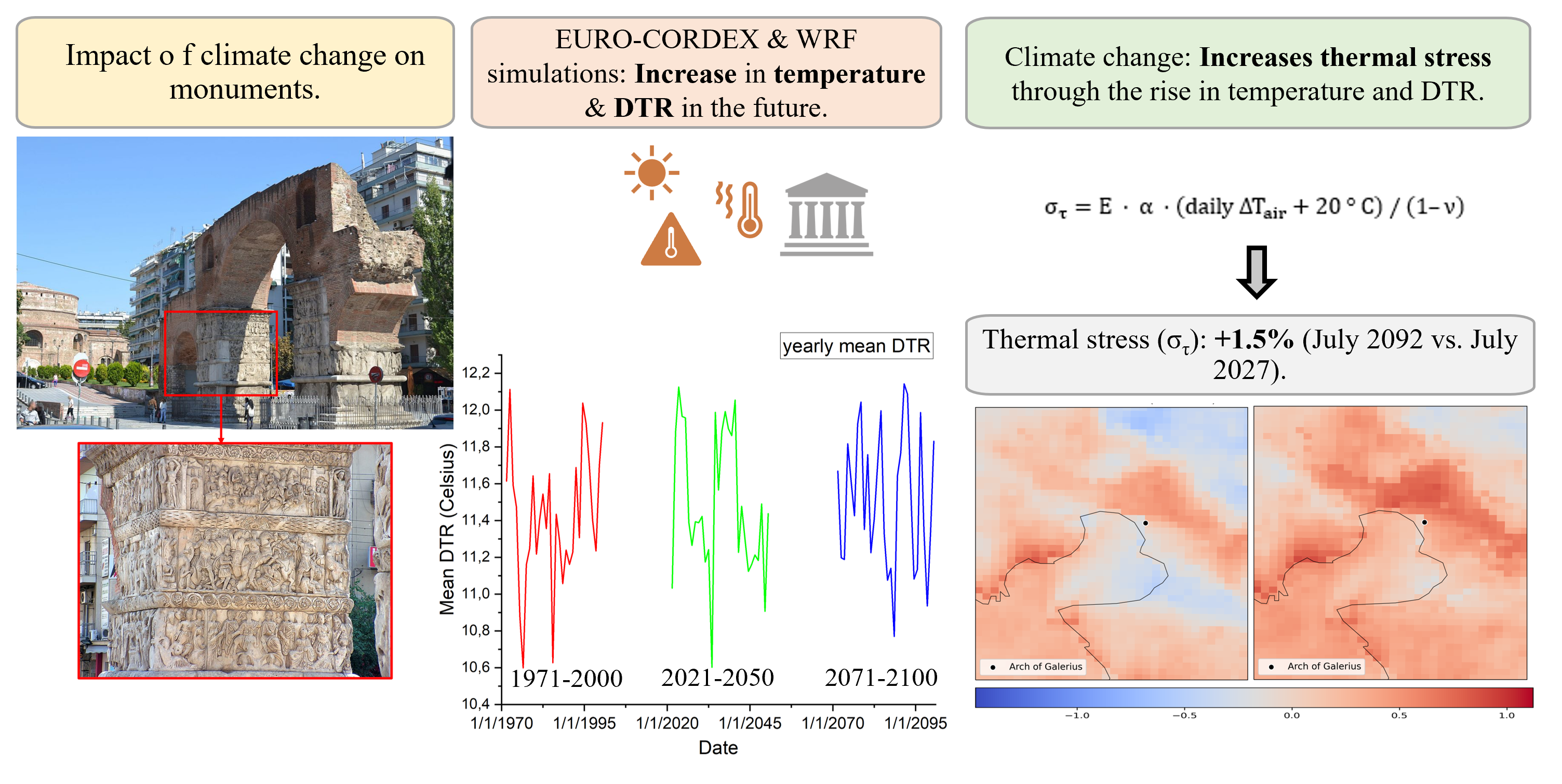
Climate change affects temperature and its variability, creating increased thermal stress on the materials of monuments located outdoors. This study investigates future temperature trends and their impact on the marble of the Triumphal Arch of Galerius in Thessaloniki, Greece, using data from the Coordinated Downscaling Experiment for European Domain (EURO-CORDEX) under the Representative Concentration Pathway 4.5 (RCP4.5) emissions scenario. The analysis compares the past period (1971–2000) with two future periods (2021–2050, 2071–2100), confirming the increase in temperature and temperature variability. High-resolution simulations (up to 1 km) of selected critical summer periods were conducted using the Weather Research and Forecasting model (WRF-ARW). The results show an increase in the number of days with significant temperature fluctuations, leading to higher thermal stress on marble. For example, during July 2092, there was an estimated 1.5% increase in thermal stress compared to July 2027. These findings highlight the importance of combining high-resolution climate simulations, future trends assessments, and analyses of climate-related impacts on structural materials. Such an approach is essential for preserving and protecting cultural heritage monuments under changing climate conditions.