- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 8 Downloads
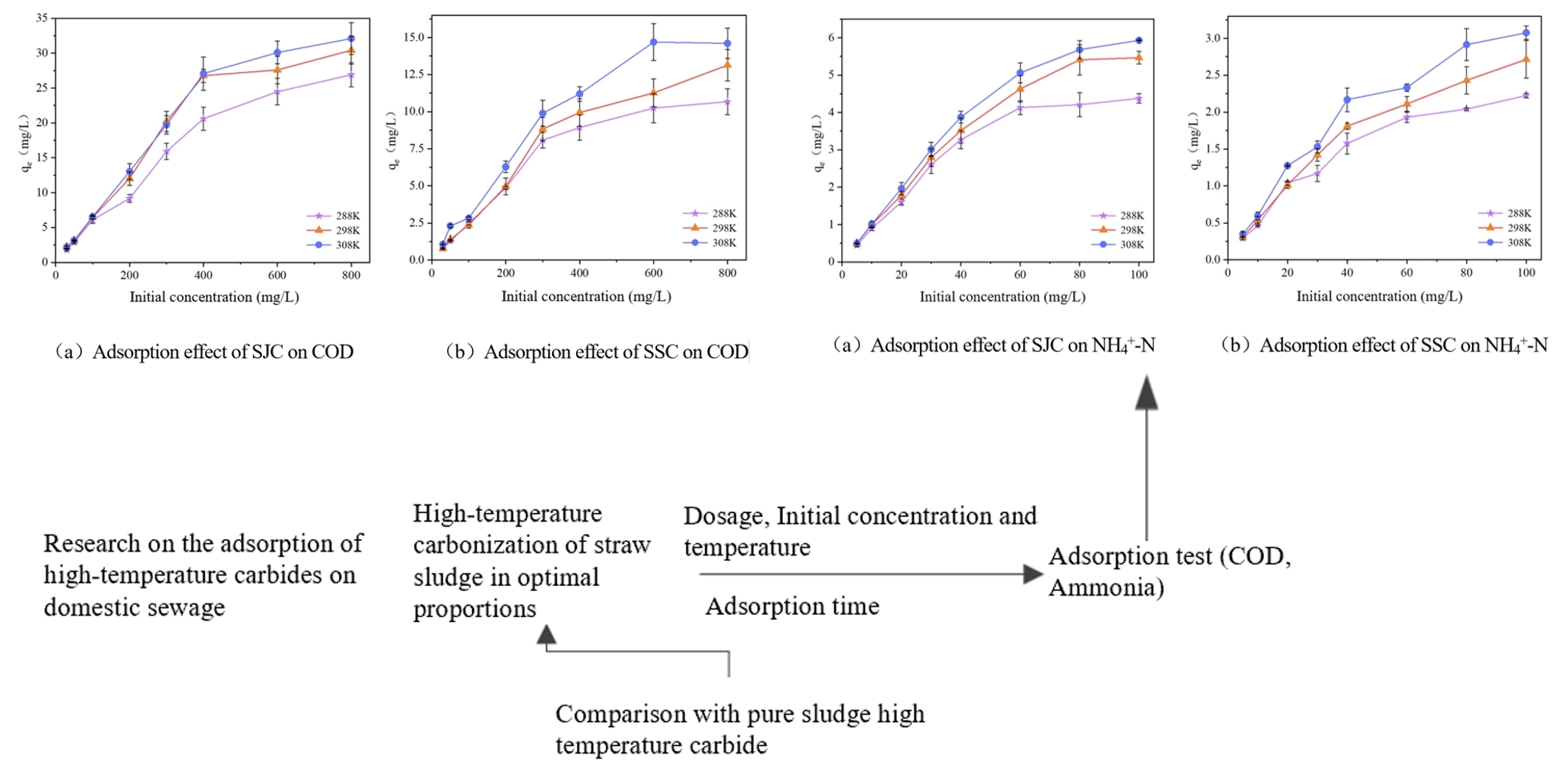
There exists a mutually reinforcing relationship between sludge and corn cob, and their combined treatment products have high potential for application. This paper focuses on the comprehensive characterization of the properties of the combined high-temperature carbonization products of sludge and corn cob and explores the effectiveness of high-temperature carbonization on the main pollutant indexes in the water treatment process. The optimal ratio (W sludge: W corn cob = 4:1) of dried corn cob sludge high-temperature carbonization (SJC) prepared at pyrolysis temperature (800℃), heating rate (5℃/min) and holding time (120 min) was used as the experimental group, and pure sludge high-temperature carbonization (SSC) was used as the control group, and the adsorption effect and adsorption mechanism of SJC and SSC on COD and NH4+-N in the concentration range of simulated domestic wastewater were investigated. The adsorption effects of SJC and SSC on COD and NH4+-N in the concentration range of simulated domestic wastewater were investigated. The results showed that the adsorption amount of COD and NH4+-N by SJC was larger than that of SSC, and the removal rate of SJC for COD solution with an initial concentration of 300 mg/L could be more than 50% at 298 K, and that of NH4+-N solution with a concentration of 40 mg/L could be up to 70%.