- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 16 Downloads
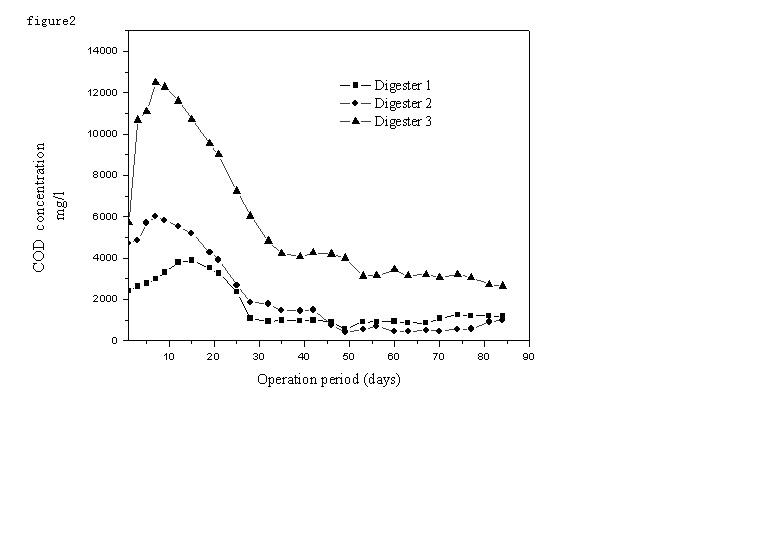
Three laboratory scale systems were operated to study the anaerobic co-digestion of sewage sludge with the excess activated sludge and cattle manure which contained low COD concentration. The experiments were performed to evaluate the effects of different methods of pretreatment. Since the poor organic substrate, the organic loading rate(OLR) was designed about 1.6kg total solids(TS)(l *d)-1 and the hydraulic retention time was controlled from 78days to 53days throughout the experiment to investigate the effects of the input on overall stability. When the digesters got stabilized, the COD removal efficiencies were 61%, 89% and 54%, respectively, and the pH value fluctuated little in the three digesters. The results indicated that the treatment of 1g volatile solids(VS) of SSEASCM on semi-continuous co-digestion generated more than 200ml of biogas on average. Thus, anaerobic co-digestion of the mixed sludge provided a means for low COD waste treatment and produced renewable energy.