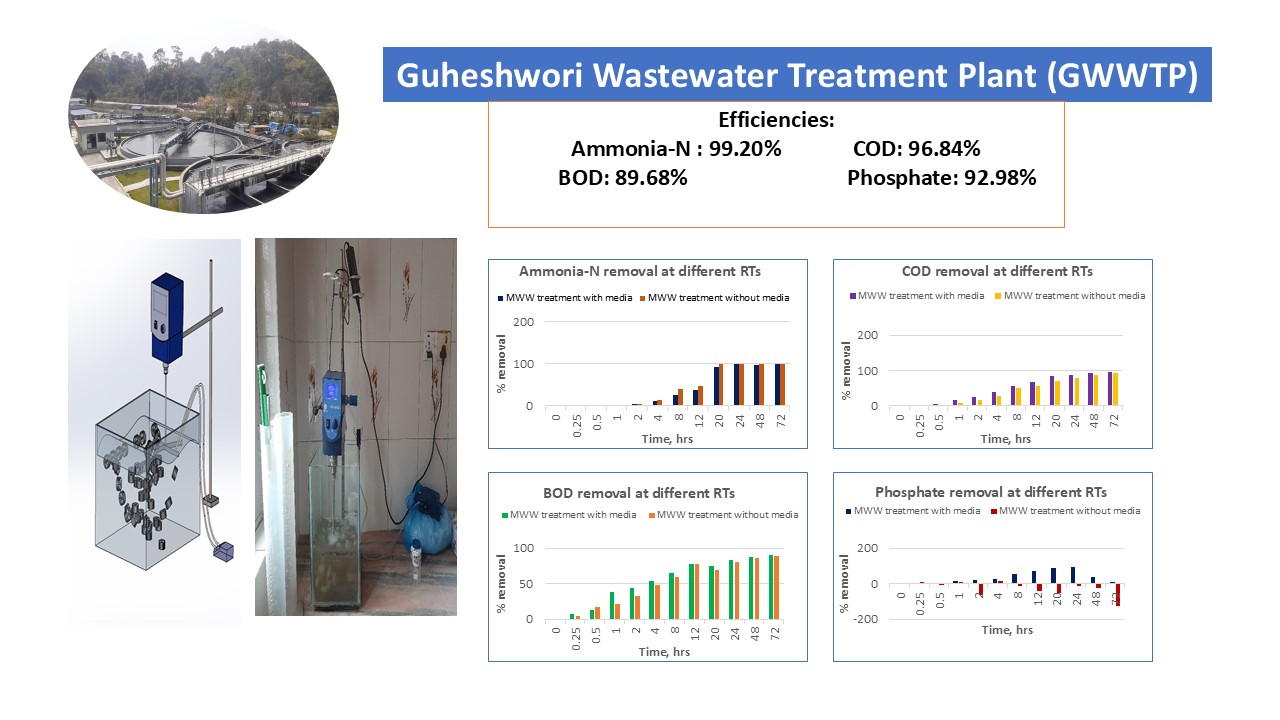
Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) technology is applicable for removing organic components and nitrogen from wastewater in the Guheshwori Wastewater Treatment Plant (GWWTP). A lab-scale single-staged aerobic batch MBBR (16L pure volume, 5L active working volume) was designed and initiated using synthetic and municipal wastewater in two phases. Removal efficiencies of COD, BOD, NH4-N, and PO43- were investigated at various retention times (0-72h) for municipal wastewater treatment with and without media. Physical parameters (pH, DO, temperature, and conductivity) were monitored under ambient conditions. Both treatments demonstrated similar BOD removals (89.68% and 88.97%) at 72h, with the treatment using media exhibiting higher COD removal (96.84%). Ammonia-nitrogen removal was completed at 20h for the treatment without media and 99.20% at 24h for the treatment with media. Phosphate removal was significant (92.98%) at 24h for MBBR with media, whereas no notable phosphate removal was observed without media. MBBR is efficient in BOD, COD, ammonia-nitrogen, and phosphate removal from municipal wastewater, offering advantages over traditional activated sludge processes regarding tank size. The findings support the feasibility of implementing MBBR for wastewater treatment at GWWTP.
Total file downloads: 42