- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 18 Downloads
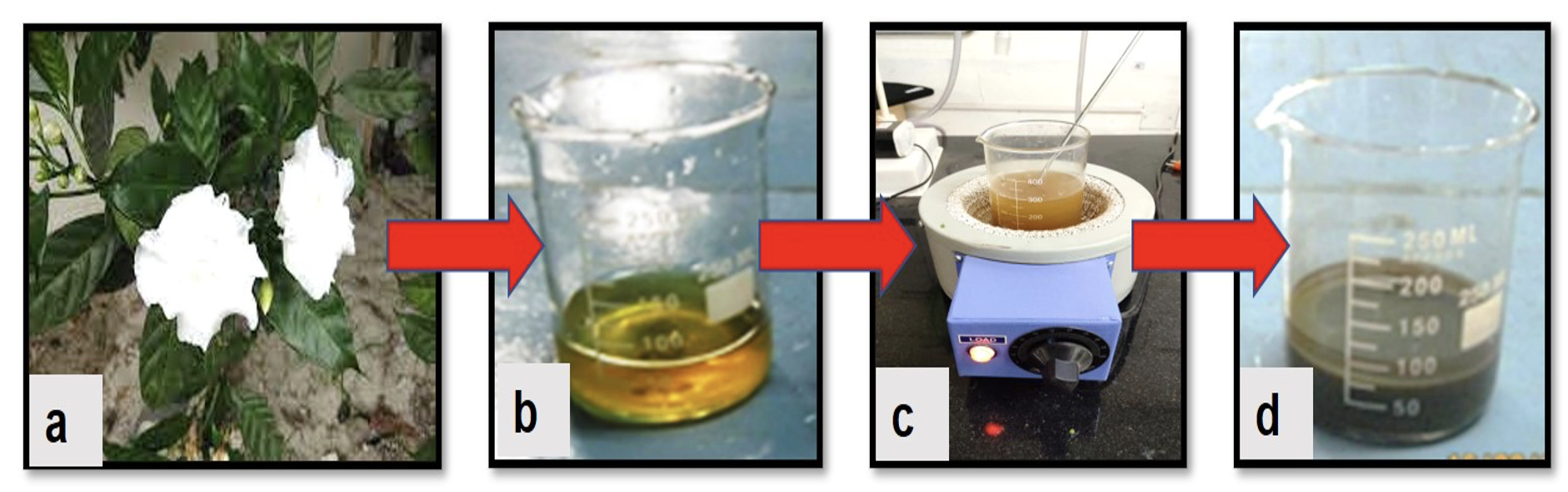
This study presents a simple, cost-effective, and eco-friendly approach for synthesizing silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using Tabernaemontana divaricata flower extract. The formation of nanoparticles was indicated by a color transition from light yellow to yellowish brown during silver ion reduction. Hybrid films incorporating chitosan and AgNPs were fabricated using liquid casting to evaluate their structural, thermal, mechanical, and optical properties. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis confirmed the formation of well-crystallized Ag nanoparticles with an average crystallite size of 0.19 nm, ensuring their effective dispersion within the chitosan matrix. Field emission microscopy revealed a uniform distribution of AgNPs on glass substrates. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) indicated that the thermal stability of chitosan nanocomposites improved, with a weight retention increase of 11% at 800°C in samples containing 9 wt.% AgNPs. Mechanical testing demonstrated a 35% increase in elongation at break, with 9 wt.% AgNPs exhibiting the highest mechanical reinforcement. Optical analysis revealed that higher AgNP concentrations resulted in reduced transmittance and enhanced absorption in the visible spectrum. These findings highlight the structural integrity and improved physicochemical properties of chitosan-AgNP nanocomposites, making them promising candidates for advanced biopolymer applications.