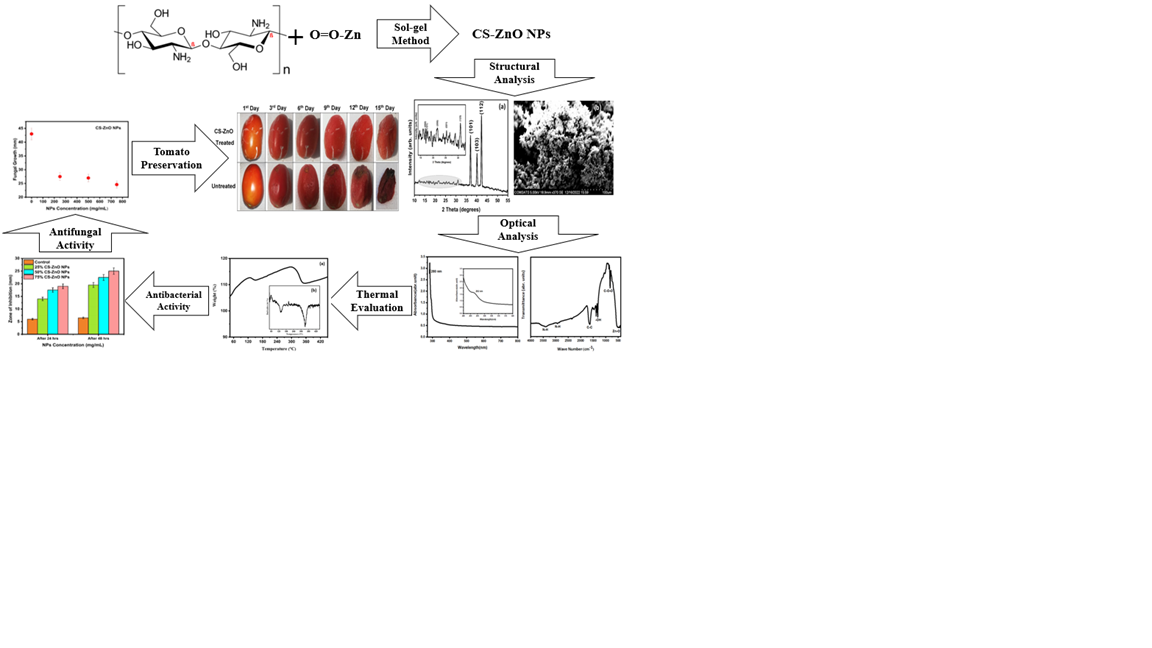
Chitosan-doped zinc oxide nanoparticles (CS-ZnO NPs) were meticulously fabricated using the sol-gel methodology. The CS-ZnO NPs underwent comprehensive analytical assessments, employing advanced techniques, encompassing X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), UV visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy, Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). An average crystallite size of 15 nm was calculated through XRD. These NPs showed an absorption band at 292 nm. TGA revealed the two-phase weight loss mechanism in the investigated nanocomposite. Effective antibacterial activity, at various NPs concentrations, was observed against Xanthomonas axanopodis pv punicea and inhibition zones of 19.5 mm, 22.5 mm, and 26 mm were calculated for 25%, 50%, and 75% NPs concentrations respectively after 48 hours of the trial. For the antifungal impact of the CS-ZnO NPs against Alternaria solani, rigorous scrutinization was performed via the agar well diffusion method. Within the vicinity of varying dosages, effective zones of 43 mm, 27.5 mm, 27 mm, and 24.6 mm indicated diverse degrees of antifungal activity. Finally, same NPs were employed as food protection agents and tomatoes were used for the purpose. Tomatoes coated with NPs showed better preservation and longer shelf life.
Total file downloads: 96