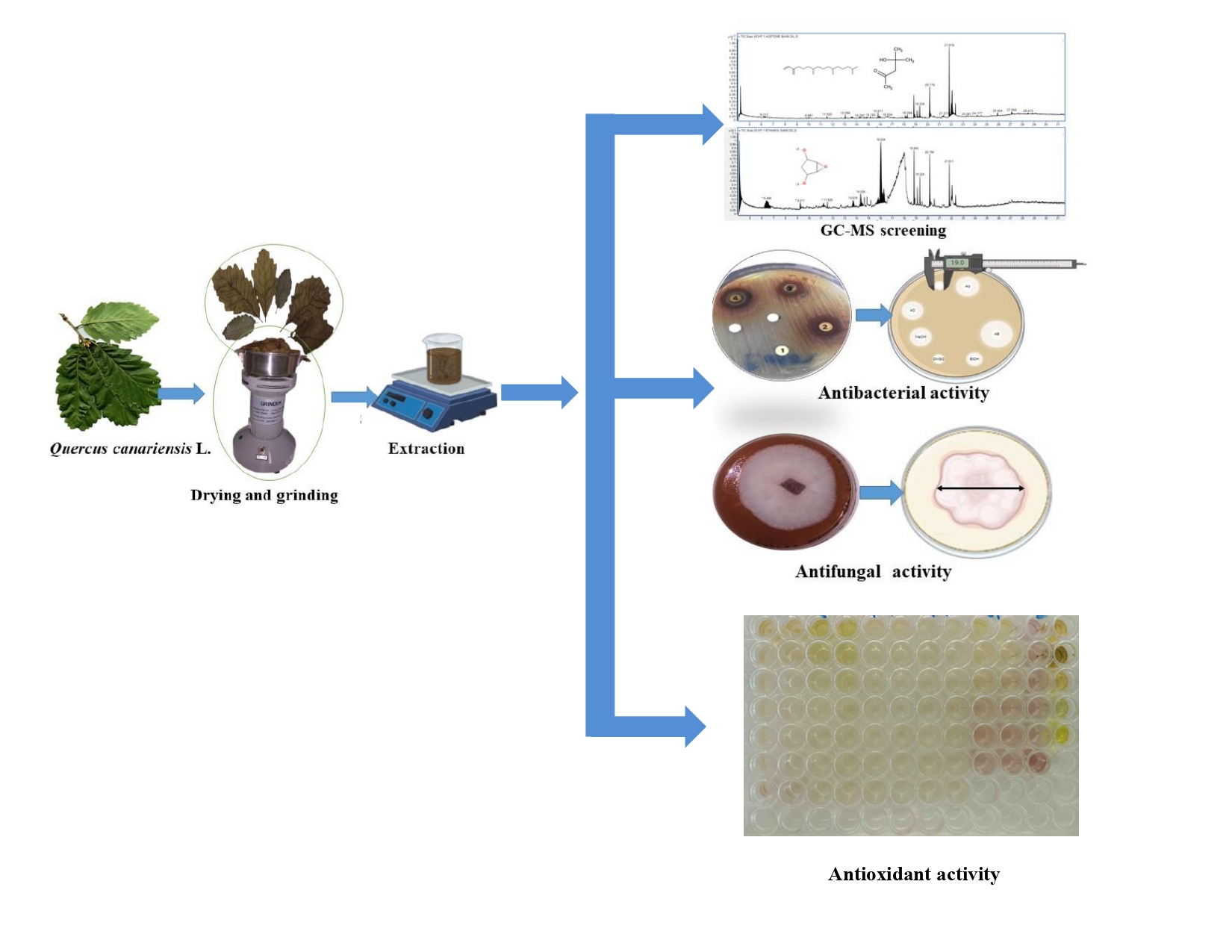
The current study was conducted to characterize the chemical composition of Quercus canariensis L. leaf extracts from Algeria and to evaluate their biological activities. The extraction was performed using solid-liquid extraction with two solvents: acetone and ethanol. The chemical profile was determined by GC-MS (Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry) analysis. Antibacterial activity was assessed using the agar diffusion method, while antifungal activity was tested using the direct contact method. Antioxidant activity was evaluated by DPPH radical scavenging. The total polyphenol content of the extracts was measured using the Folin-Ciocalteu reagent, yielding the following values: ethanol (9.90 ± 0.05 mg GAE/g) and acetone (9.55 ± 0.11 mg GAE/g). Phytochemical analysis revealed that Quercus canariensis L. contains a mixture of diterpenes, fatty acids, cyclopentones, and quinic acid. In the acetonic extract (AcE), 16 compounds were detected, making up 97% of the total extract. The dominant compounds were 2-Pentanone, 4-hydroxy-4-methyl (25%), Neophytadiene (22%), and n-Hexadecanoic acid (10%). The ethanolic extract (EtE) contained 58% of identified compounds, with 6-oxabicyclo[3.1.0]hexane-2,4-diol (28%) as the major constituent. The antibacterial activity study demonstrated that the acetone extract had a substantial inhibitory effect against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus, with inhibition zones exceeding 21 mm. The evaluation of antifungal activity indicated that both the acetone and ethanol extracts exhibited high activity against Aspergillus brasiliensis, with inhibition rates of 57.47% and 54.02%, respectively. All extracts demonstrated a DPPH scavenging ability. The ethanolic extract had the lowest IC50, hence demonstrating the strongest antioxidant activity with an inverse IC50 of 2.63 mg/mL compared to the acetone extract. These findings suggest that the extracts of Quercus canariensis L. possess strong antimicrobial properties and may serve as promising sources for future pharmaceutical applications.
Total file downloads: 54