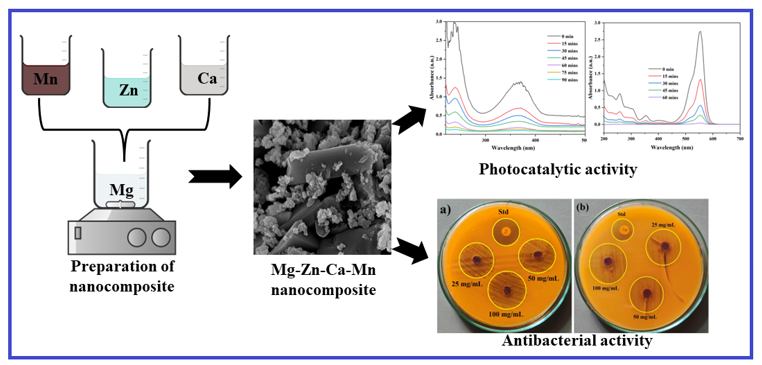
The current work elucidates the significance of nanometal oxide composite for enhanced environmental remediation applications. An efficient photocatalyst has been prepared by preparing the multi-metal oxide nanocomposite by combining MgO, ZnO, CaO, and MnO2 NPs during the synthesis process. The nanocomposite was prepared using a simple sol-gel method, mixing each precursor and NaOH as a reducing agent. XRD analysis confirms the composite's high purity and crystallinity, revealing a cubic MgO and CaO phase alongside hexagonal ZnO and MnO2 phases, with a calculated crystallite size of 19.74 nm. FESEM analysis reveals a rod-like MgO structure surrounded by agglomerated spherical ZnO, CaO, and MnO2 particles, indicating strong surface charge interactions. EDX confirms the successful formation of a pure nanocomposite. UV-Vis spectroscopy confirmed distinct absorption peaks at 226 nm (MgO), 273 nm (MnO2), 313 nm (CaO), and 382 nm (ZnO), indicative of the coexistence of multiple oxides within a single matrix. The results confirm the formation of Mg-Zn-Ca-Mn nanocomposite with excellent physio-chemical properties. Additionally, the nanocomposite demonstrates excellent antioxidant activity, stabilizing DPPH radicals with a maximum scavenging efficiency of 97.45% at 100 mg/mL. Under sunlight irradiation, it achieves 99.68% degradation of Rhodamine B in 60 minutes and 98.55% degradation of Amlodipine in 90 minutes, following pseudo-first-order kinetics. Reusability tests confirm its structural and functional stability over five cycles, reducing degradation efficiency by only 4.1% for Rhodamine B and 5.3% for Amlodipine. The characterizations and observations indicated that the prepared nanocomposite can be an excellent source for environmental remediation applications.
Total file downloads: 15