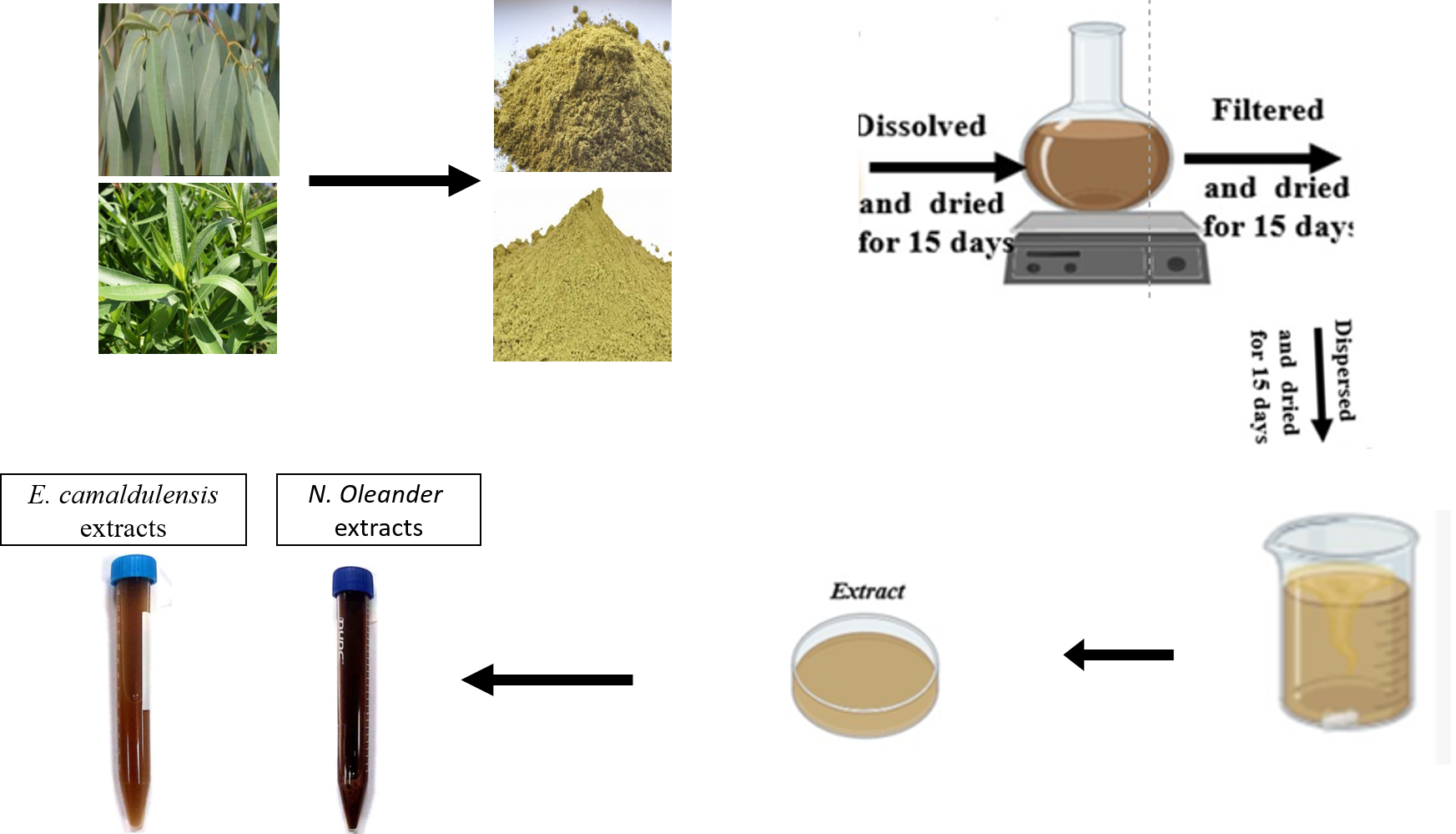
Herbs are abundant sources of therapeutic compounds with significant potential in the global pharmaceutical industry. This study focused on analyzing the phytochemical composition, specifically phenols, flavonoids, and tannins, and their antioxidant properties in methanolic extracts from four selected medicinal plants: Nerium oleander (NO), and Eucalyptus camaldulensis (EC). The total contents of phenolic compounds, flavonoids, and tannins were quantified using standardized methods. Antioxidant activity was assessed through the DPPH radical scavenging assay. The analysis confirmed the presence of phenols, flavonoids, and tannins in all extracts. Notably, E. camaldulensis exhibited the highest concentrations of total phenolics and flavonoids (5.57 ± 0.22 mg GAE/g and 1.38 ± 0.06 mg QE/g, respectively). All extracts demonstrated strong antioxidant activity against DPPH and ABTS radicals, with IC50 values ranging from 0.55 to 49.43 µg/mL and 0.65 to 13.7 µg/mL, respectively. Additionally, E. camaldulensis showed significant anticoccidial effects. The findings suggest that these medicinal plant extracts could serve as valuable an antioxidant and anticoccidial agents for drug development.
Total file downloads: 12