- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 24 Downloads
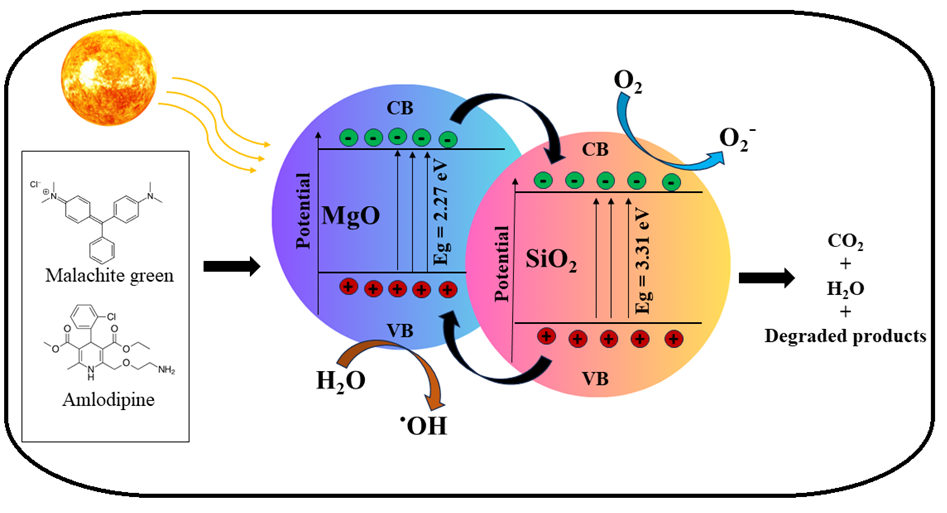
This article represents the photocatalytic activity of harmful pollutants from textile and pharmaceutical industries and compares the photocatalytic efficiency between pure MgO and MgO – SiO2 nanocomposite. The MgO NPs are synthesized using hydrothermal synthesis, in which the extract from Nerium oleander flowers is utilized as a reducing agent. The SiO2 NPs were synthesized from the natural source of bamboo leaves by sol-gel method. Then, the composite is made by simply stirring and sonicating MgO and SiO2 NPs. Then the prepared nanocomposite and pure MgO were analyzed for the crystalline nature (XRD), morphology (FE-SEM), particle size (DLS), Functional groups (FTIR), elemental composition (EDAX), optical properties (UV-vis spectroscopy). The above studies provide excellent MgO NPs and MgO – SiO2 composite characteristics. The prepared MgO and MgO - SiO2 were utilized for the photocatalytic activity of textile and pharmaceutical pollutants up to 90 and 120 mins, respectively, under sunlight irradiation. After degradation, the photocatalysts were tested to find their stability and reusability for five cycles. As discussed above, the MgO – SiO2 performs better than pure MgO regarding pollutant degradation and stability. The prepared MgO and MgO – SiO2 have been examined for antibacterial activity, exposing better results than the standard antibacterial agent (Streptomycin).