- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 28 Downloads
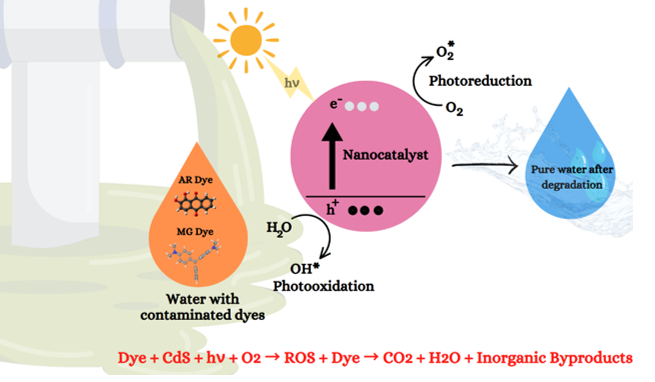
The increasing release of textile dyes into water bodies poses a significant environmental challenge due to their toxicity and resistance to degradation. In this study, cadmium sulfide (CdS) nanoparticles (NPs) and niobium (Nb)-doped CdS at three different concentrations were synthesized using a green synthesis approach, employing Syzygium cumini seed extracts as eco-friendly reducing and capping agents. The results confirmed the formation of a wurtzite hexagonal phase, with decreasing crystal size. However, as the crystal size decreased, the bandgap increased to 2.60 eV due to the quantum confinement effect. The FE-SEM analysis revealed distinct morphologies influenced by Nb doping levels and EDAX confirms the sample purity. Photocatalytic studies under visible light demonstrated significant dye degradation for both Alizarin Red and Malachite Green. CdS-N3 exhibited the highest kinetic rate constants of 2.03 and 2.32×10−2 min−1 for Alizarin Red and Malachite Green, respectively, with degradation efficiencies of 84.97% and 88.76%. Furthermore, Nb doping enhanced the stability, with CdS-N3 maintaining 79.9% and 84.1% degradation efficiency after five cycles for Alizarin Red and Malachite Green, respectively. Additionally, NPs shown significant antibacterial activity against gram-positive bacteria, highlighting their potential for dual-function environmental remediation. The synergistic effects of Nb doping were found to enhance both photocatalytic degradation and antibacterial performance, making these materials promising candidates for sustainable wastewater treatment and microbial control.