- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 10 Downloads
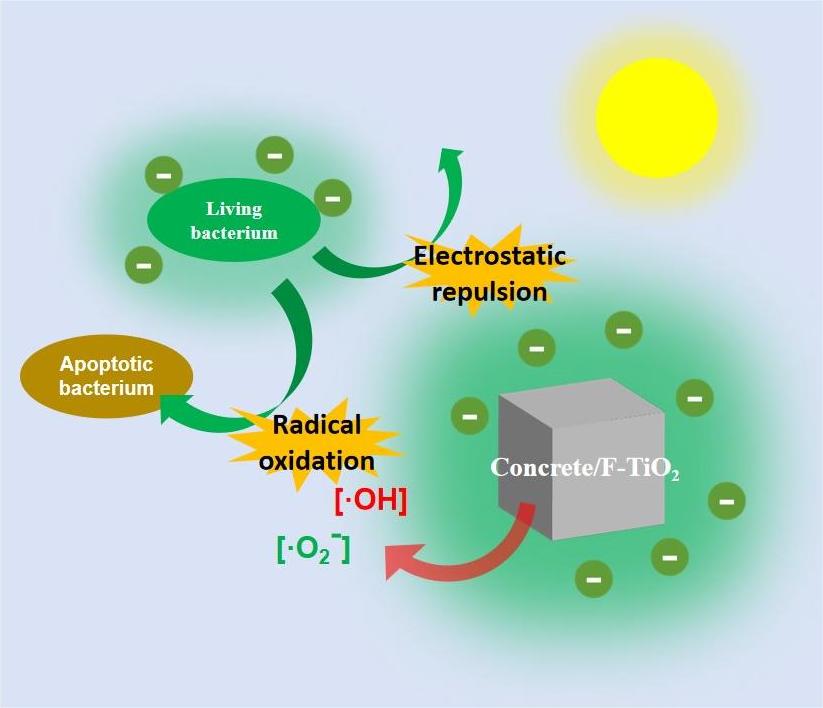
Sponge cities embody a green and sustainable urban development approach, with permeable concrete structures crucial for collecting natural precipitation. Over time, however, microbes from rainwater can adhere to and proliferate on these concrete surfaces, potentially accelerating material corrosion and posing health risks. To combat this, our study introduces a straightforward and effective antimicrobial surface strategy. We applied a fluorine-modified titanium dioxide photocatalyst coating to permeable foam concrete surfaces. The fluorine regulation enhances electron transfer to the titanium dioxide, creating a negatively charged interface. This charge repels negatively charged microbes electrostatically and curbs microbial growth through the oxidative properties of photogenerated radicals. Tested under 50 mW/cm2 of simulated sunlight, the bacterial count at the negatively charged interface was just 35.7% of that at a positively charged interface, with the coating retaining about 90% of its antibacterial efficacy even in highly contaminated conditions. This research offers a cost-effective and efficient method for developing antimicrobial coatings for building materials.