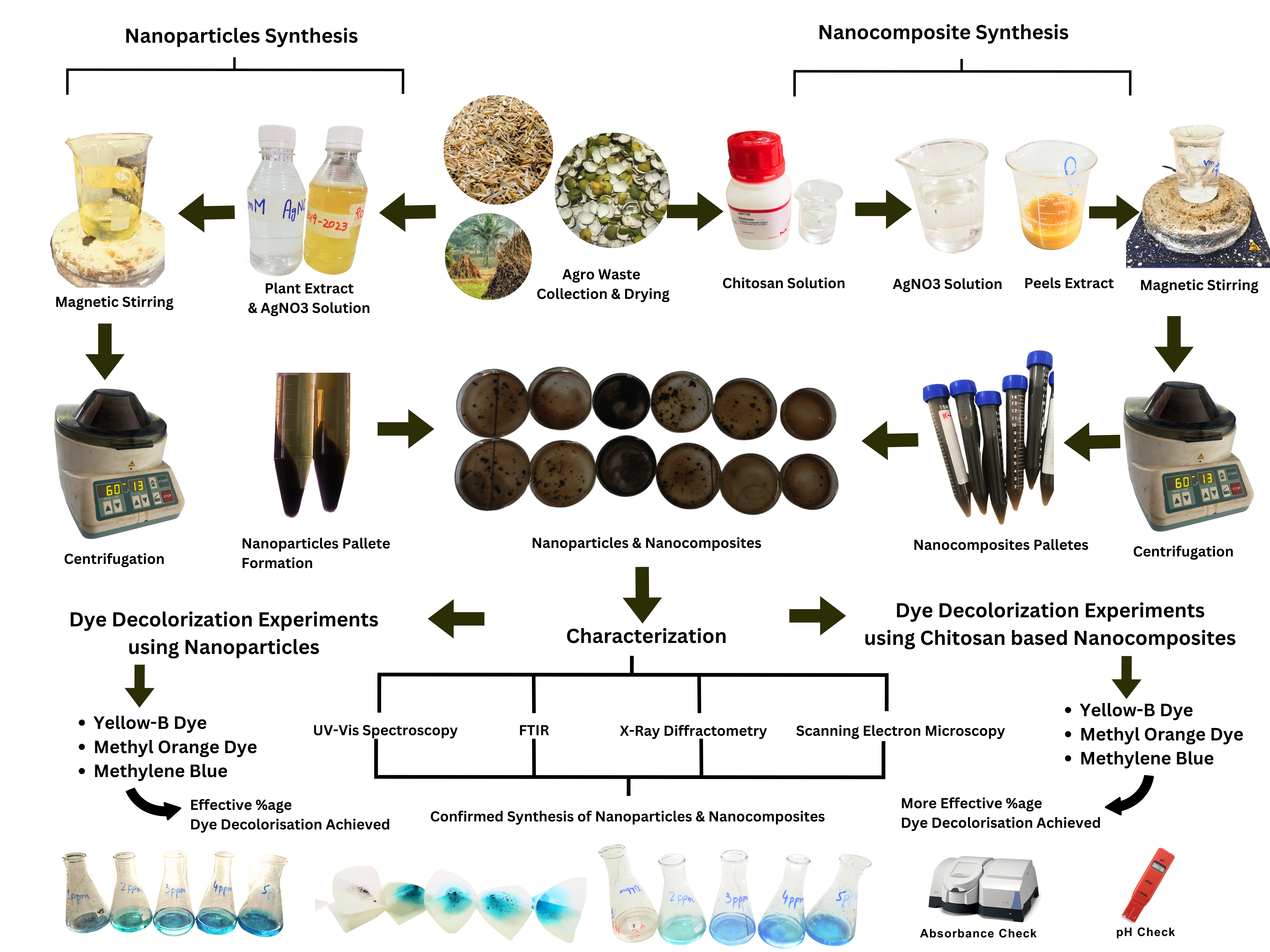
Green nanotechnology is a multidisciplinary field that has emerged as a rapidly developing research area, serving as an important technique that emphasizes on making procedures that are clean, non-hazardous, and especially environment friendly, in contrast with chemical and physical methods currently employed for nano-synthesis. The present work concentrated on the green synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) and Chitosan based Silver Nanocomposites (CS-AgNCs) using aqueous extracts of some indigenous plants; optimizing the different experimental factors required for the formation and stability of AgNPs and CS-AgNCs. The optimum conditions were found to be 0.05 M and 0.1 M concentration of silver nitrate solution, a 1:10 ratio extract of the peels, and an incubation period of 24-48 h at 4 °C. The synthesized AgNPs were characterized using UV-VIS Spectroscopy, XRD, FTIR, and SEM and CS-AgNCs were characterized by UV-VIS Spectroscopy and FTIR. FTIR analysis showed the presence of polyphenolic functional groups which confirmed the biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles. Furthermore, these nanoparticles and their composites showed promising properties for the decolorization of azo dyes. Nanoparticles and nanocomposites of Citrus paradisi peels showed 100% decolorization of Methylene Blue, while the nanocomposites of Oryza sativa husk showed more decolorization about 80 % than its nanoparticles having 47 % of the same dye. Hence, they can be a very good choice for application in targeted environmental remediation e.g., industrial wastewater treatment.
Total file downloads: 59