- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 11 Downloads
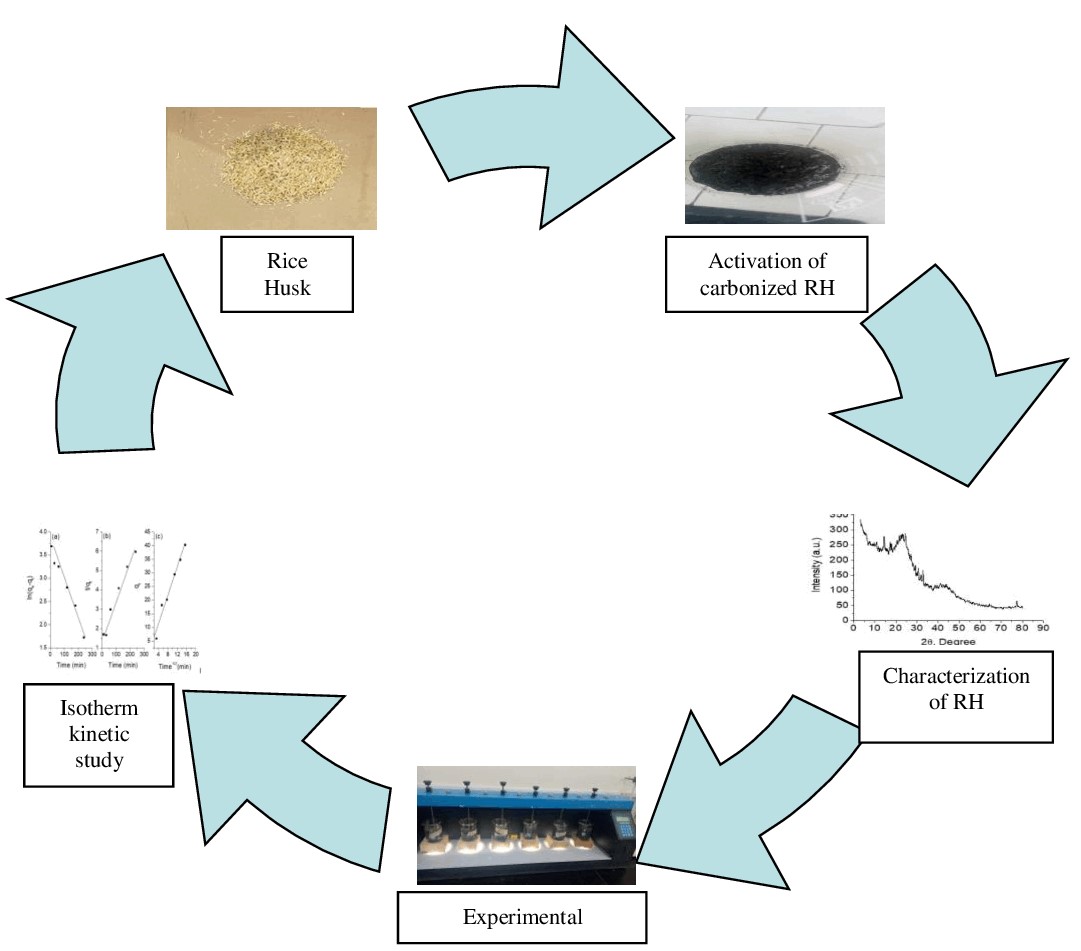
Olive mill wastewater (OMWW) contains many phenolic compounds that if discharged without proper treatment, may lead to substantial risks to human health and deterioration of the environment and aquatic systems. In this study, an attempt was made to produce activated carbon from Rice Husk (RH). The RH was chemically activated by calcium chloride and was utilized for the removal of phenol from the aqueous solution. The removal efficiency using the Activated Rice Husk (ARH) was investigated at different variables such as pH, contact time, adsorbent dose, initial concentration, and carbonization temperature. Results showed that the optimum removal efficiency was 91.62% which was achieved at pH=6, carbonization temperature=850 ˚C, and after 4hrs contact time. Adsorption isotherm fitted well to Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models while the kinetic data fitted well to the pseudo-second-order model, and thermodynamic data showed that the adsorption is endothermic in nature. Then the activated rice husk sample was used for phenol removal from real OMWW samples from different locations in the city of Irbid-Jordan providing average removal efficiency reached 94.6%. The study indicates that RH and ARH have good potential to be used for phenol removal.