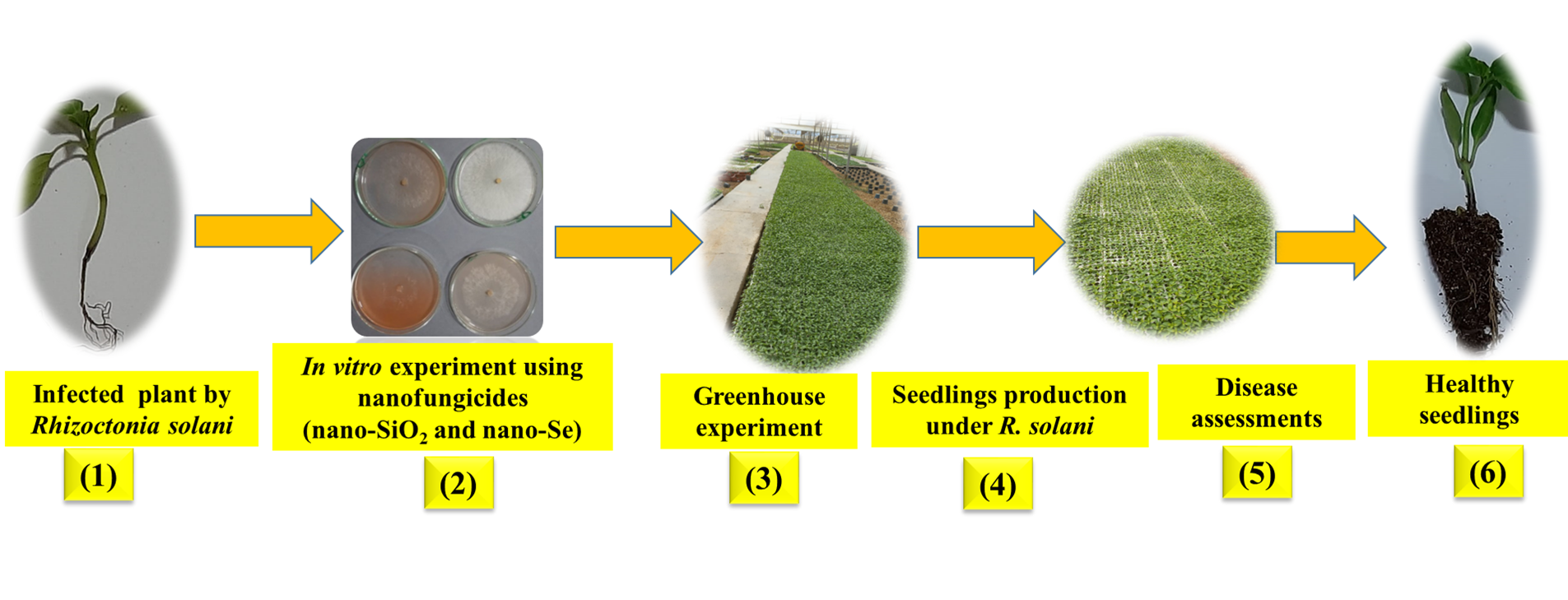
There is an urgent need to find sustainable alternatives to chemical pesticides for protecting the environment and healthy food as well as enhancing seedlings quality. Therefore, the current study is an attempt to find nano-alternatives to chemical fungicides for protecting pepper seedlings (Capsicumannuum L.) production from the phytopathogen of Rhizoctonia solani and to promote pepper seedlings’ growth and quality by individually applying n-SiO2, n-Se and combined n-SiO2 and n-Se together under the nursery conditions. Single and combined applied doses of nano-silica (200 mg L-1) and nano-selenium (100 mg L-1) were treated pepper seedlings for controlling the root rot disease of R. solani. Applied nanosilica (200 mg L-1) was showed the maximum values in the studied vegetative growth of pepper seedlings, enzymatic antioxidants and the photosynthetic parameters under the fungal infection. The suggested mechanism of applied nano silica in boosting the growth of pepper seedlings against R. solani was confirmed by the SEM images of infected seedlings (control) and treated ones by nanosilica. The same trend was observed of such behavior of enzymatic antioxidants after treatment by nanosilica resulting from enhancing the resistance of pepper seedlings against studied fungal pathogen. This priority was followed by the nano-Se, then the combination of both. This study, as a new report as we know, opens a new window towards the possible nanofungicides against the studied fungal pathogen (R. solani) to reduce the application of chemical fungicides and ameliorate pepper seedlings growth and quality. Further research is needed concerning new nanoparticles and new phytopathogens.
Total file downloads: 5