- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 11 Downloads
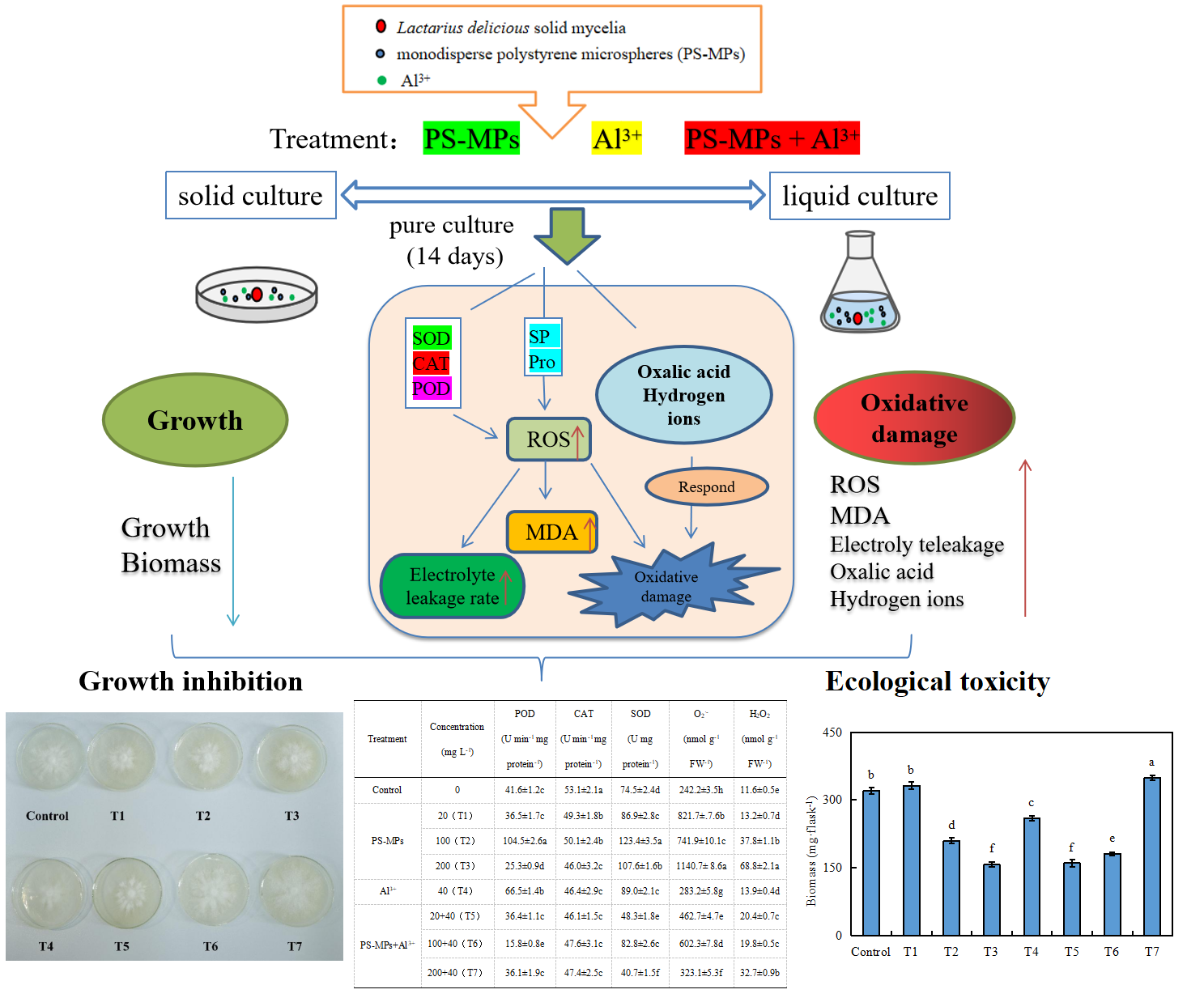
To investigate the combined toxic effects of microplastics and aluminum (Al) on ectomycorrhizal fungi, Lactobacillus delicious (Ld) was selected as the experimental subject to conduct research on monodisperse polystyrene microplastics (PS-MPs) (0, 20, 100, 200 mg L-1) and Al3+ (40 mg L-1) single pollution on Ld growth, the antioxidant system and organic acid secretion, followed by their combined effect. The results showed that the growth of Ld was inhibited and the biomass decreased significantly (P < 0.05) under single exposure to PS-MPs or Al3+, and the contents of superoxide anion radical (O2·-) and H2O2 in mycelia increased significantly (P < 0.05). Meanwhile, superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (POD) activities were also significantly increased (P < 0.05), while catalase (CAT) activity was significantly decreased (P < 0.05), indicating that PS-MPs or Al3+ stress had different effects on antioxidant enzyme activities in Ld mycelia, which used highly active antioxidant enzymes to eliminate excess reactive oxygen species (ROS) and maintain their dynamic balance. In addition, the electrolyte leakage rate, proline and malondialdehyde (MDA) contents in Ld mycelia were significantly increased (P < 0.05). Under the combined exposure of PS-MPs and Al3+, compared with the control group, the combined exposure of high concentrations of PS-MPs and Al3+ (200+40 mg L-1) had a certain promoting effect on the biomass of Ld. In addition, the O2·-, H2O2, electrolyte leakage rate and malondialdehyde content in Ld mycelia increased significantly (P < 0.05), but these indices were significantly lower than those in the single PS-MPs exposure group at the same concentration. This indicates that the combined effect of PS-MPs and Al3+ could reduce the damage of single pollutants to the Ld biomass membrane and reduce the production of ROS to a certain extent. In addition, correlation analysis showed that H2O2 in Ld mycelia had a highly significant positive correlation with the oxalic acid and total hydrogen ion concentrations in the culture solution (P < 0.01). This indicates that strain Ld could respond to the oxidative damage caused by microplastics and Al by secreting oxalic acid and hydrogen ions into the culture medium.