ABSTRACT
Termites, highly structured social insects of the order Isoptera, are major biological threats to
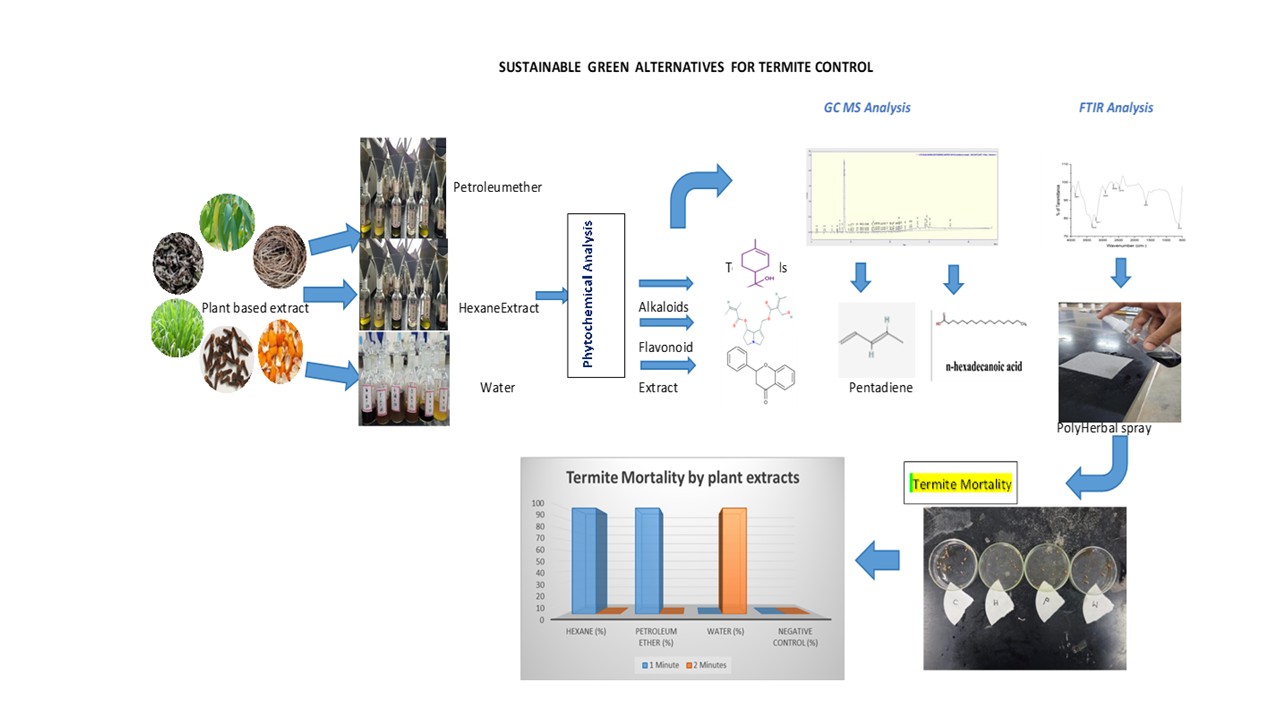
wooden infrastructure, agricultural products, plantations, and stored materials. Although chemicalinsecticides are widely used, their long-term application has led to increasing termite resistance,environmental degradation, and toxicity to non-target species. These drawbacks emphasize thegrowing need for eco-conscious, biodegradable alternatives. Plant-based biopesticides, rich inbioactive metabolites, offer a sustainable and safer approach to termite management.This studyexplores the insecticidal potential of six botanicals—Eucalyptus globulus, Cymbopogon citratus,Syzygium aromaticum, Artemisia absinthium, Citrus sinensis, and Chrysopogon zizanioides—using petroleum ether, hexane, and distilled water as extraction media. Phytochemical analysisconfirmed the presence of key secondary metabolites, including alkaloids, saponins, flavonoids,steroids, carbohydrates, terpenoids, phytosterols, and quinones, while polyphenols,anthraquinones, and cardiac glycosides were absent. Advanced GC-MS profiling identified majorconstituents such as pentadiene and hexadecanoic acid, and FTIR spectroscopy revealed functionalgroups like hydroxyl (O–H), alkene (C=C), halogenated chains (C–C), amines (N–H), and alkylaryl ethers. A distinctive aspect of this research is the comparative solvent-based assessmentshowing extremely rapid anti-termite activity. Hexane and petroleum ether extracts achieved 100%termite mortality within one minute, while aqueous extracts reached full lethality in twominutes.These findings establish the remarkable efficacy of solvent-optimized plant formulationsas natural, fast-acting, and environmentally sustainable alternatives to conventional synthetictermiticides paving the way for safer pest control strategies in agricultural and structural settings.
Keywords: Termite Control, Plant-Based Extracts, Phytochemical Analysis, GC-MS Analysis, Sustainable Pest Management.
Total file downloads: 11