- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 3 Downloads
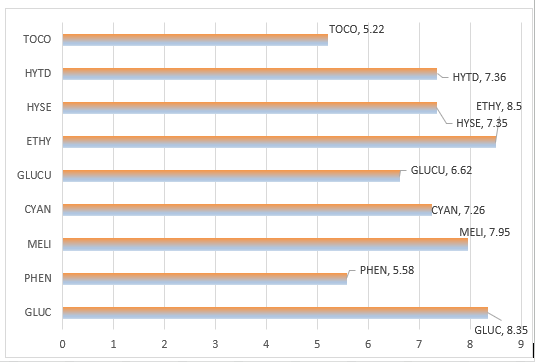
The active components of Jordanian Peganum harmala L. (P. harmala) were investigated using both GC-MS and DFT calculations. The study focused on the methanol extract of P. harmala leaves, which was found to contain 21 significant natural components, of which 9 compounds constituted more than 2% of the total composition. These 9 compounds, including α-D-Glucopyranose (GLUC), Phenobarbital (PHEN), Melibiose (MELI), Cyanuric acid (CYAN), D-Glucuronic acid (GLUCU), Ethylamine (ETHY), 3-Hydroxysebacic acid (HYSE), 3-Hydroxytetradecanedioic acid (HYTD), and α-Tocopherol (TOCO), were evaluated as eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors for Al (Aluminium), Fe (Iron), and Cu (Cooper) metals using DFT calculations. The results showed that TOCO had the highest anti-corrosion performance among the 9 compounds, with Fe exhibiting the most inhibitory activity compared to Al and Cu. The high electrophilicity and Gibbs free energy of adsorbate value on metal surfaces made TOCO a distinguished corrosion inhibitor. The HOMO and LUMO gap of the inhibitors decreased in the following order: ETHY > GLUC > MELI > HYTD > HYSE > CYAN > GLUCU > PHEN > TOCO. These findings suggest that these chemicals may serve as environmental-friendly anticorrosion inhibitors for metal surfaces, although more in vitro experiments are needed to confirm these results.