- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 14 Downloads
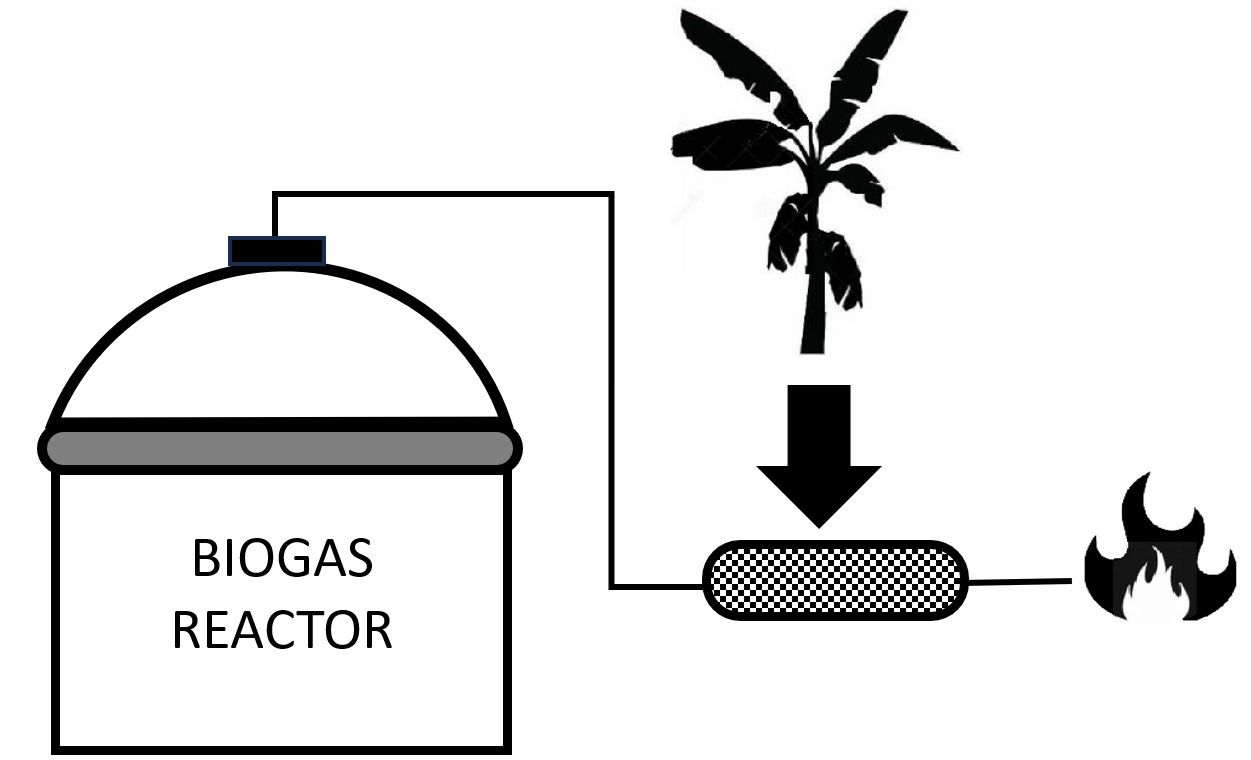
Biogas, an alternative technology that produces environmentally friendly fuels, usually contains impurities which may infer the performance of combustion. Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) gas is one of the impurities in the biogas. This study’s objective is to assess the removal of hydrogen sulfide using banana leaves. Dry and wet banana leaves were selected to remove pure H2S gas using simple arranged equipment. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDX) analysis was also performed to establish the effect of H2S adsorption on the surface of banana leaves. The adsorption capacity was determined using the adsorption isotherm equation. Wet banana leaves have a higher H2S gas adsorption efficiency then dry banana leaves. Based on the SEM image, the morphology of the banana leaves after adsorption shows that there are more materials attached to the surface of the leaves than before adsorption. The adsorption capacity of wet leaves is 1.25–1.29 times greater than those of dry leaves, based on the Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms. Based on this study, banana leaves have the potential to be used as an impurity remover for H2S in biogas. Further research with real biogas stocks is needed to obtain their true efficiency.