- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 20 Downloads
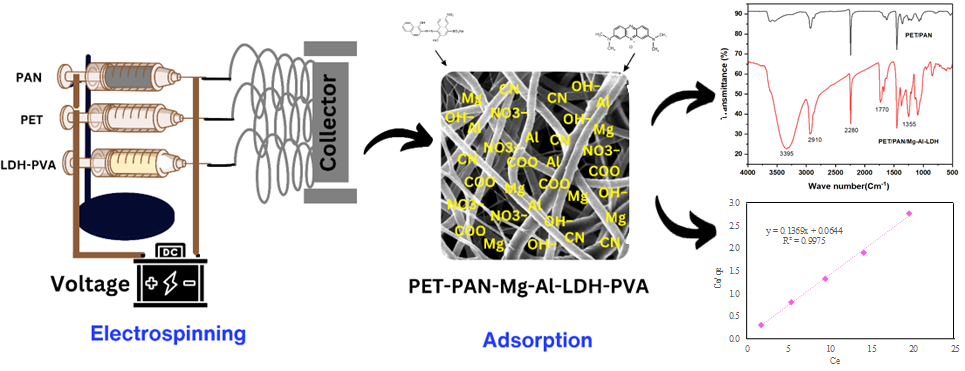
The current work reveals the fabrication of a novel nanofiber composite membrane of PET-PAN modified with Mg-Al-LDH-PVA through electrospinning process. The nanocomposite membranes characterization was conducted with different techniques i.e. SEM, EDS, FTIR, XRD, and water contact angle to evaluate the structure and surface morphology. The optimized nanomembrane was utilized as a useful adsorbent for removal of toxic anionic dye Eriochrome Black T (EBT) and cationic dye Methylene blue (MB) from wastewater. Experimental results identified that PPLP3 membrane has a potential for the removal of EBT (83%) and MB (52%) at pH 3 and 7, respectively, from aqueous solution. The optimum adsorption capacity of PPLP3 nanocomposite membrane was identified and calculated as 7.3 mg.g-1 followed by the pseudo 2nd order kinetics and Langmuir adsorption isotherm fit well with R2 values of 0.964 and 0.997, respectively. The synthesized nanocomposite membrane could be utilized for effective adsorption of contaminations from different wastewaters.