- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 23 Downloads
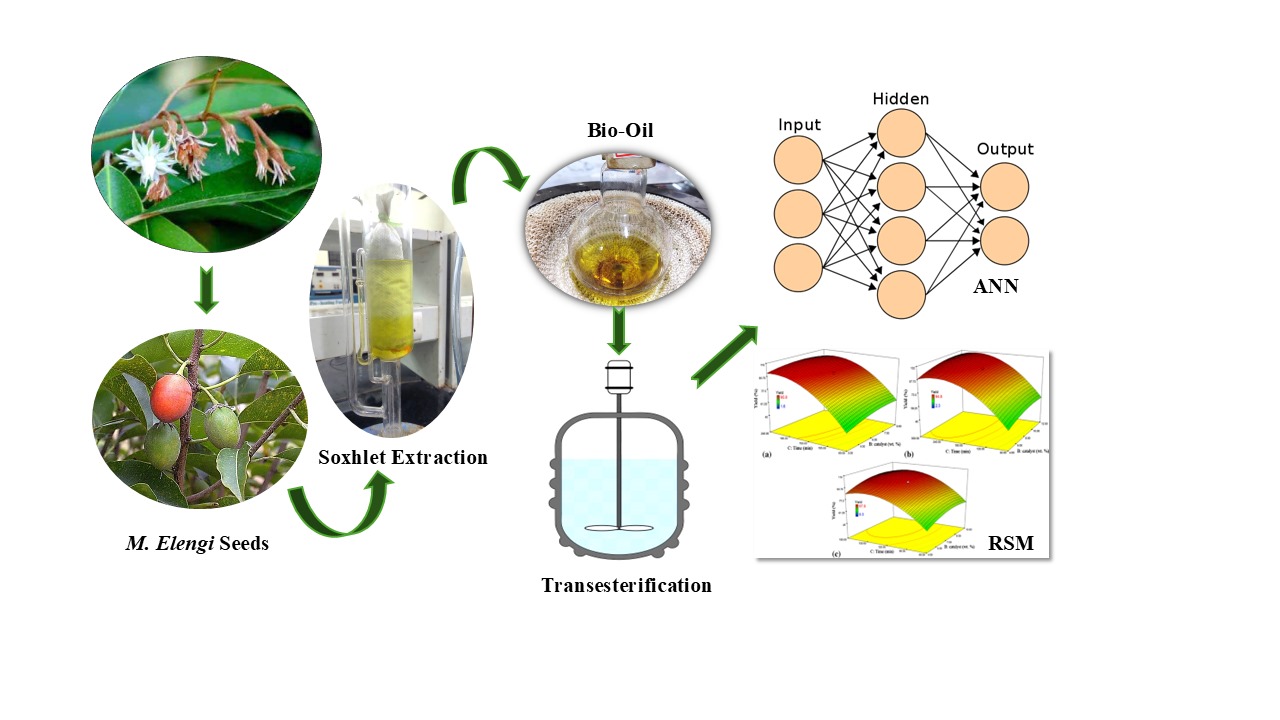
The present paper mainly focused on the statistical optimization of biodiesel production from the non-edible seed of Mimusops Elengi using a potassium hydroxide-catalyzed Transesterification process. Consequently, it compares the prediction and simulating efficiencies of the Response Surface Method (RSM) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) for biodiesel yield achieved via the Transesterification process. In this experimental reaction, various process variables influencing the transesterification process were analyzed: methanol oil ratio, catalyst concentration, reaction temperature, and time. In the both statistical analysis RSM and ANN studies obtained an R2 values of 0.9923 and 0.9992 respectively. The optimum biodiesel yield achieved was 83% at a 1:7.5 molar ratios of methanol and m.elengi seed oil using potassium hydroxide as a base catalyst.