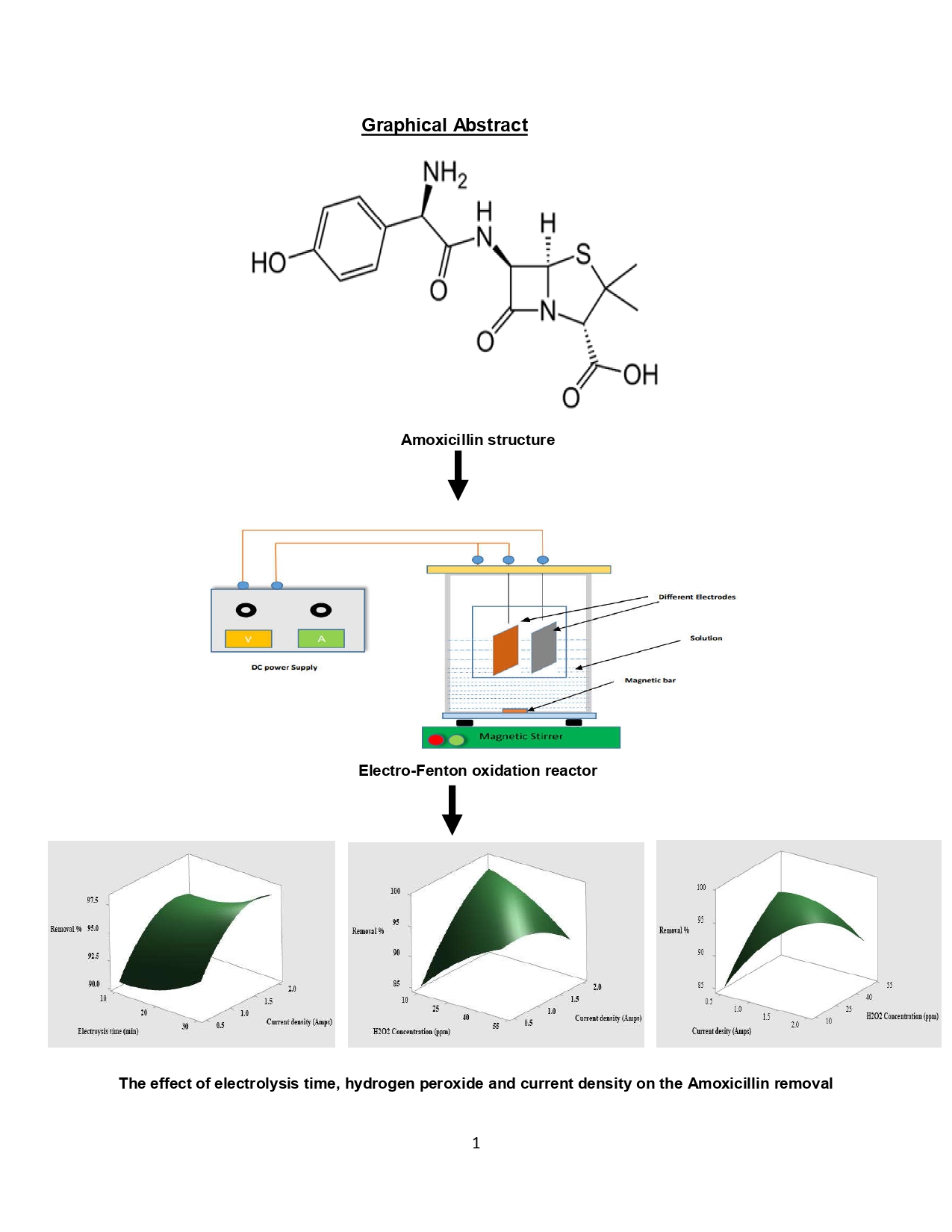
The purpose of this work is to examine the efficiency of the Electro-Fenton process (Fenton oxidation) for the elimination of amoxicillin from simulated wastewater through response surface methodology (RSM). The effect three operating parameters that were selected for this evaluation were electrolysis time, hydrogen peroxide concentration, and the current density. The Electro-Fenton method was assessed by a set of experiments that were designed using the Box-Behnken model. The results conclude optimum parameters conditions, at 30 min electrolysis time, 30 ppm H2O2, and current density 2 amps by fixing the other two parameters; 20 ppm concentration of amoxicillin and pH of 3. The maximum removal efficiency at these conditions was 98.11%. The mathematical model concluded has a high correlation coefficient (R2= 98.3). Depending on the results, the Electro-Fenton process has proven an excellent method for the elimination of antibiotics from wastewater.
Total file downloads: 20