- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 27 Downloads
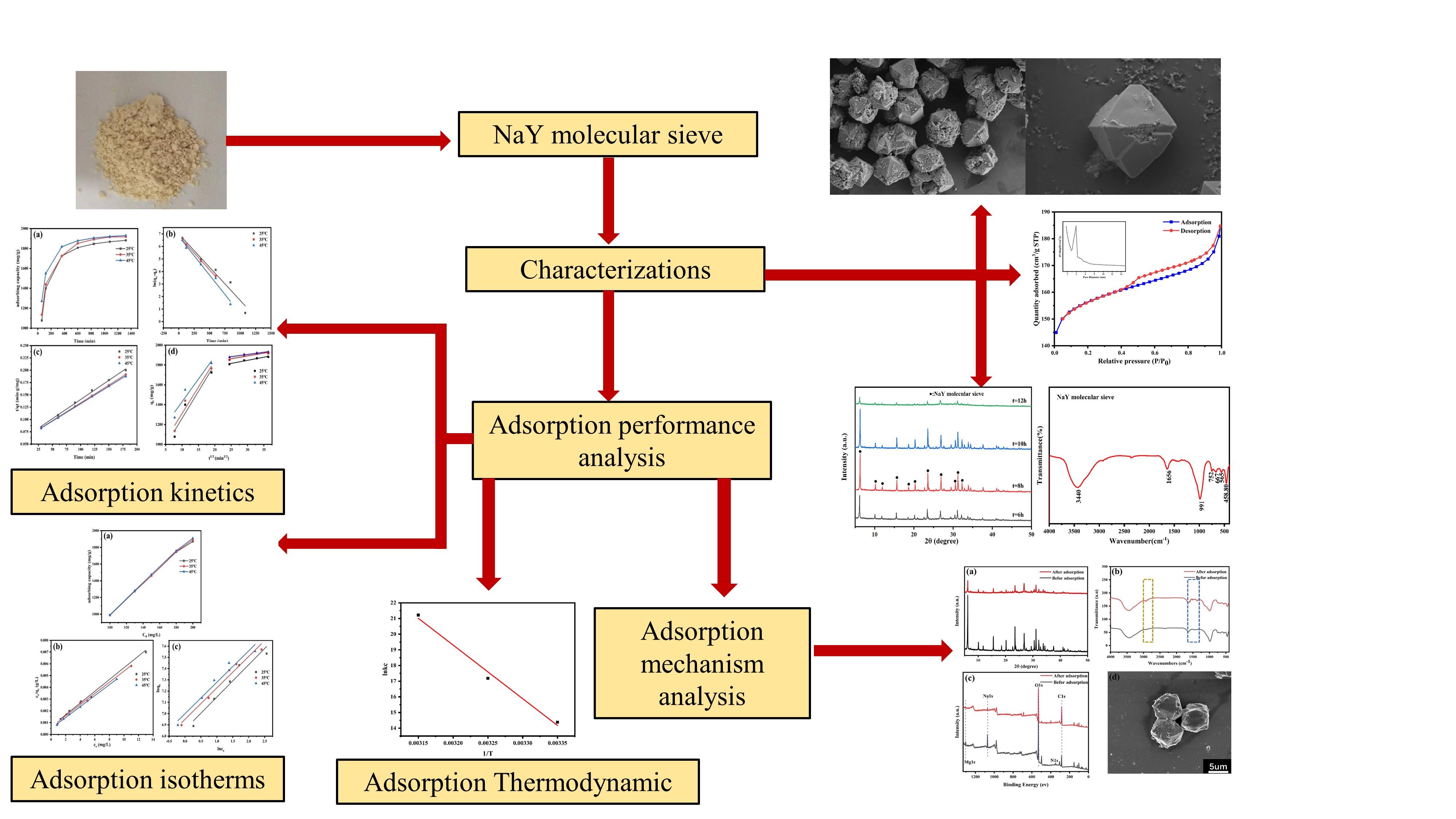
The synthesis of NaY molecular sieve from coal gangue and its adsorption properties for malachite green were studied. The process adopts high-temperature sintering hydrothermal method, which not only improves the utilization rate of coal gangue, but also analyzes the key parameters affecting the formation of molecular sieve with high adsorption efficiency of organic pollutants, and characterizes the materials by XRD, SEM, EDS, BET, etc. The adsorption process of malachite green solution was analyzed by adsorption kinetics and isotherm, and the adsorption mechanism was elucidated by XRD, FTIR, XPS and SEM. The results show that the maximum adsorption capacity of NaY molecular sieve for malachite green is 1910mg/g under the best conditions, which conforms to the quasi-second-order kinetic equation and Langmuir isothermal adsorption model.