- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 40 Downloads
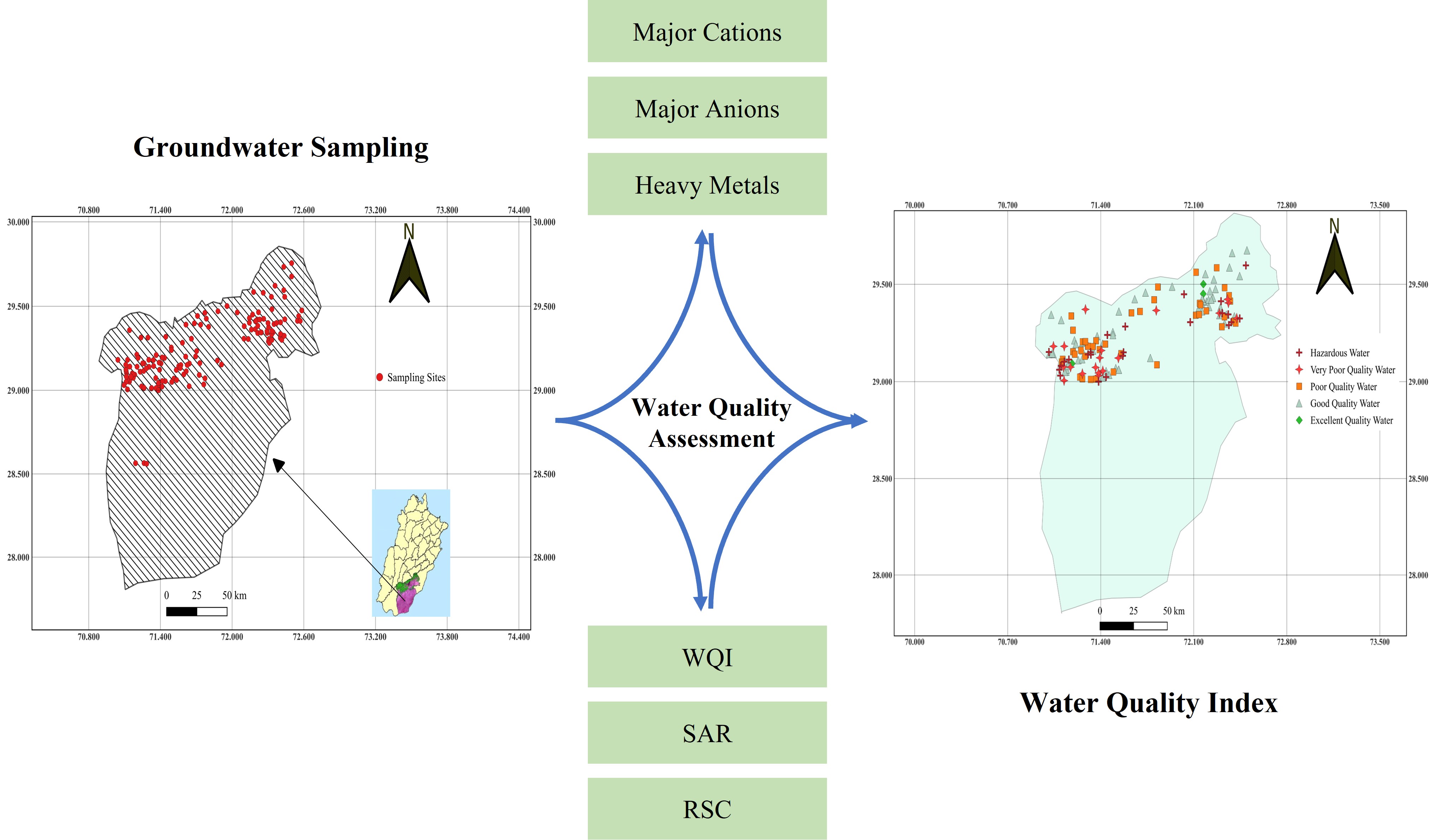
As the groundwater pollution is increasing, it is crucial to assess groundwater quality and characterize hydrogeochemistry accurately for long term water supply. In this study groundwater samples were collected from 120 locations from Bahawalpur district and analyzed for electrical conductivity (EC), pH, total dissolved solids (TDS), sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (Ca2+), magnesium (Mg2+), carbonate (CO3-), bicarbonate (HCO3-), sulfate
(SO42-), chloride (Cl-), nitrate (NO3-), fluoride (F-) and heavy metals. The results obtained from the analysis of samples showed that the SAR of nearly 65% of samples collected from Bahawalpur district were in acceptable limit (<6 meq L-1), while 12% found to be unfit for irrigation (>10 meq L-1). Similarly, the RSC values depicted that 8% samples were unfit while 64% samples were falling in the category of fit irrigation water. Most of the water samples were predominantly Ca2+-HCO3- and Na+-HCO3- type, that were controlled by various processes of cation exchange, water-rock interaction, dissolution and evaporation. Some samples fall in the middle of diamond and lower triangles of Piper diagram are showing no dominant type of water (mixed water type) due to the complex influence of rock-water interactions as well as anthropogenic activities. The Water Quality Index (WQI) showed that out of total 120 sampling sites in Bahawalpur the number of excellent water samples were only 2% while 18% water samples were characterized as hazardous. Moreover, the number of samples falling in the categories of good, poor and very poor quality water were 36%, 29% and 13% respectively.