- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 53 Downloads
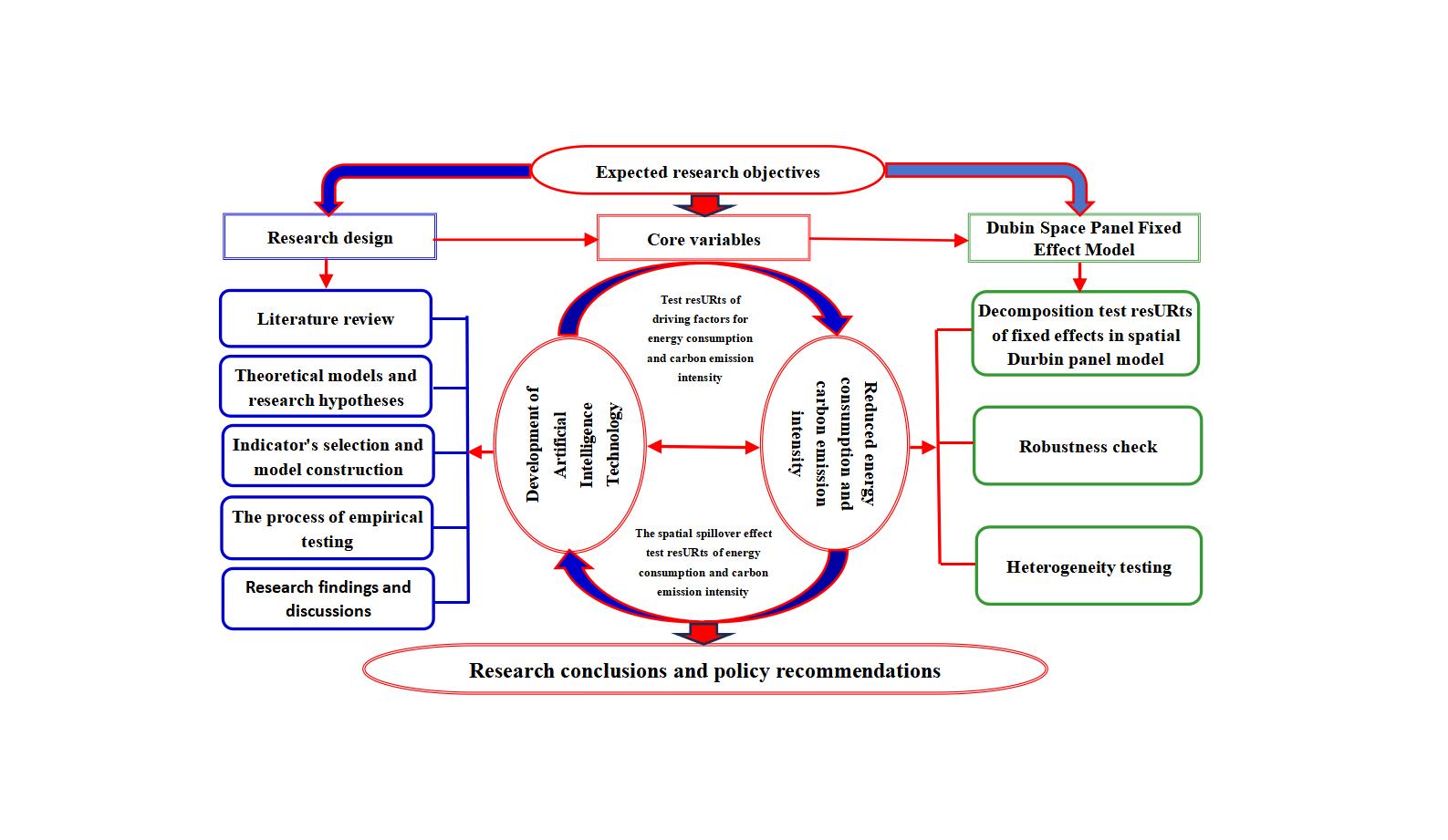
This paper investigates the impact of artificial intelligence technology on energy consumption carbon emission intensity and its spatial effect in Chinese provinces. By analyzing the 2012-2021 data of 30 provinces and cities in China, this paper constructs a spatial Durbin panel model to test the direct and indirect effects of the application of AI technology on energy consumption and carbon emission intensity. The results show that artificial intelligence innovation development index, digital finance index, and the environmental regulation intensity reduce the provincial energy consumption carbon emission intensity, while Per capita GDP level, urbanization rate, and industrial energy consumption intensity significantly increase the energy consumption carbon emission intensity. In addition, industrial structure upgrading and industrial technological progress, as mediating variables, have a significant inhibiting effect on carbon emission intensity. The study concludes that the application of AI technology can effectively reduce provincial carbon emission intensity by optimizing energy consumption and carbon emission scenarios, thus promoting the goal of green and low-carbon development in China.