- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 42 Downloads
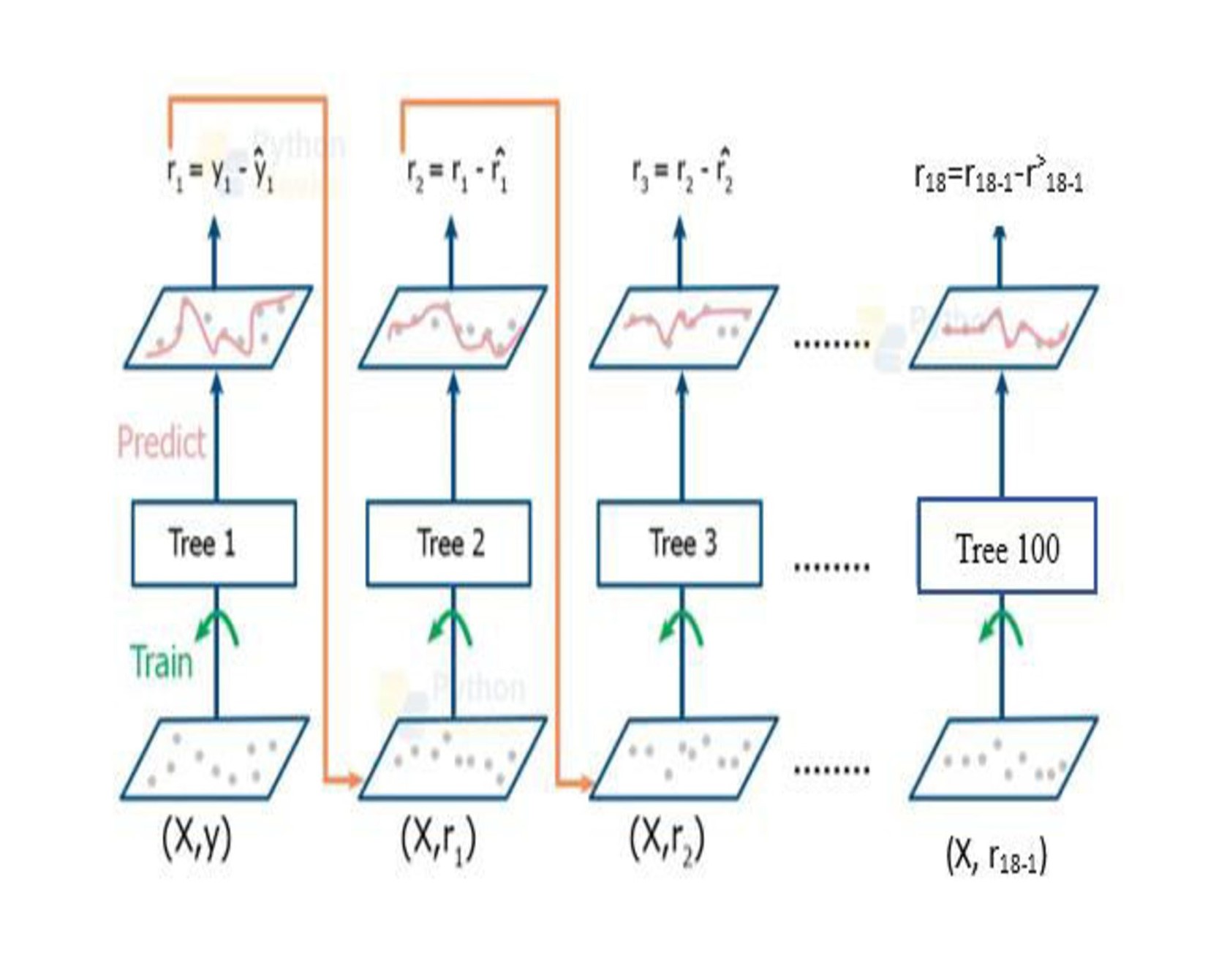
Among the most significant issues that will impact and pose a major threat to our future are global warming and climate change. This study focuses on forecasting India's carbon emissions, specifically examining the role of agriculture and agri-related industries, using time-series data from 1990 to 2020. To achieve this, a machine learning-based approach was proposed, utilizing five advanced models AdaBoost, XGB, Gradient Boosting, Random Forest, and Linear Regression. These models were selected for their ability to process large datasets, identify complex patterns, and provide precise predictions, offering a comprehensive framework for estimating carbon emissions. The approach aims to identify the most accurate predictive model for estimating carbon emissions, facilitating informed policy interventions and strategic planning. The Carbon Budget 2023 research highlights that India's carbon emissions increased by 8.2% in 2023, raising significant concerns for environmental sustainability. Using the proposed machine learning models, the study facilitates robust data prediction. Among the five models, XGB demonstrates superior performance with evaluation metrics such as a Mean Absolute Error (MAE) of 19843, Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 24022, Mean Squared Error (MSE) of 5770998, R² value of 0.9, and test accuracy of 99%. These findings establish XGB as the most reliable model for forecasting carbon emissions. Consequently, XGB emerges as a powerful tool for accurately estimating emissions and addressing the challenges posed by climate change.