- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 23 Downloads
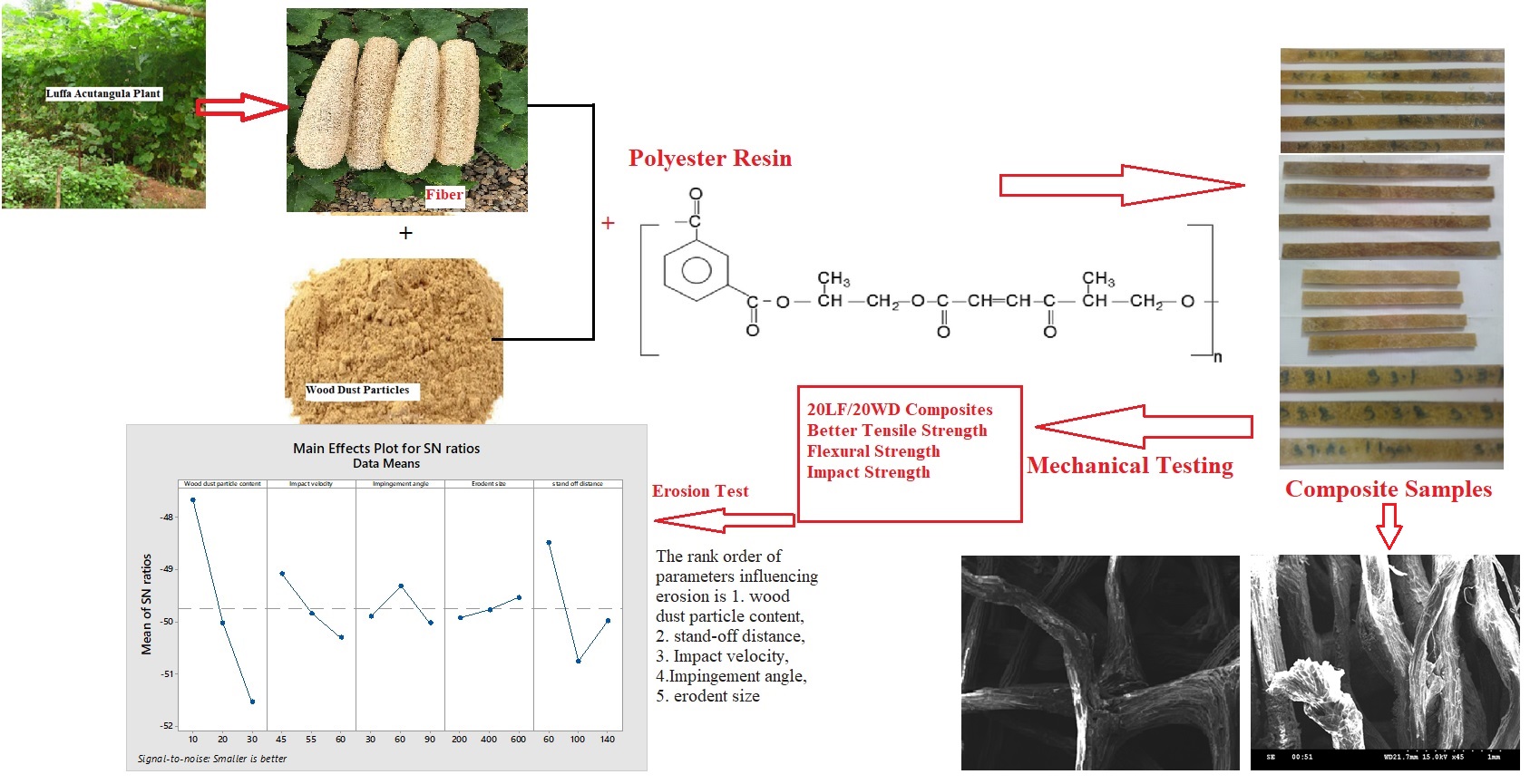
This study investigates the effect of teak wood dust (TWD) particles on the mechanical properties and erosion wear characteristics of Luffa acutangula fiber (LAF) reinforced phenol formaldehyde (PF) composites. Test samples were prepared with 20% LAF and varying TWD content (5%, 15%, and 25%). The addition of 15% TWD showed a significant improvement in mechanical performance, with tensile strength increasing by 17.56%, flexural strength by 48.78%, and impact strength by 54.64%. The optimum parameters for minimizing erosion wear were determined using Taguchi analysis, achieving a minimum erosion rate of 199.82 mg/Kg. This combination included 15% TWD, 40 m/s impact velocity, 60° impingement angle, 450 µm erodent size, and 60 mm standoff distance. Inspired by signal processing and classification methodologies, this study employs a structured approach to enhance mechanical and erosive wear properties, akin to wavelet-based data optimization techniques. The results demonstrate that TWD particles significantly improve the properties of natural fiber-reinforced composites, presenting a novel, sustainable material solution for industrial applications. This study provides a novel approach to enhancing composite materials by integrating TWD into LAF/PF composites, offering sustainable solutions for lightweight and durable industrial applications. These composites hold potential for applications beyond traditional industries, extending to biomechanical systems and prosthetic design, where lightweight and durability are critical, much like EMG-based gesture recognition systems in human-machine interaction.