- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 28 Downloads
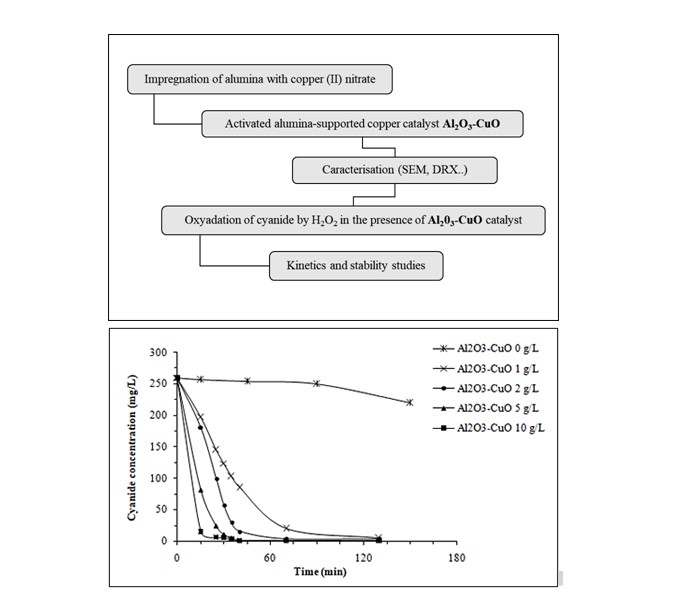
Cyanide compounds are widely used in some electroplating, chemical and metallurgical industries. They are often found in their liquid discharges. This work highlights the performance of an activated alumina-supported copper catalyst in the removal of cyanide by oxidation with hydrogen peroxide in aqueous solution. The influence of catalyst dose, initial molar ratio of hydrogen peroxide/cyanides, temperature, and catalyst reuse was studied. The activated alumina-supported copper significantly enhanced the reaction rate showing a good catalytic activity. The efficiency of cyanide elimination was increased after 30 minutes of oxidation from 48% to 98% by increasing the catalyst dose from 1 to 10 g/L. Rising the temperature from 30°C to 40°C promoted cyanide removal. The catalyst can be recycled four times and show good stability. The kinetics of cyanide oxidation was revealed to be pseudo-first order with regarding cyanides. The rate constants as well as the activation energy were determined.