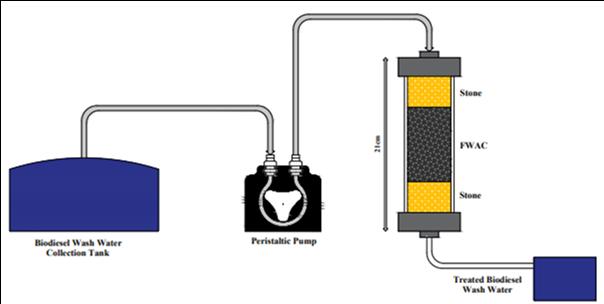
In work illustrated, the mixed food reject was carbonized and further activated with zinc chloride for biodiesel washwater treatment experiments. Biodiesel washwater is one of the significant side streams generated during biodiesel production from waste cooking oil. The food waste activated carbon (FWAC) and commercial activated carbon (CAC) were analyzed for structural and surface morphology using X-ray diffraction (XRD), Filed emission scanning microscopy (FE-SEM) and IR-Raman spectroscopy. The adsorption experiments were performed at 10 to 50 minutes with an adsorbent dosage of 0.1 to 0.5 in 100 mL of biodiesel wash water. pH, Turbidity and Total dissolved solid of biodiesel plant effluent before and after adsorption experiments were determined. Food waste-activated carbon used for the study reduced the effluent pH from 11.5 to 7, Turbidity from 435 NTU to 1 NTU and TDS from 1140 mg/L to 145 mg/L. The feasibility of NaOH recovery from biodiesel wash water was also studied.
Total file downloads: 14