- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 26 Downloads
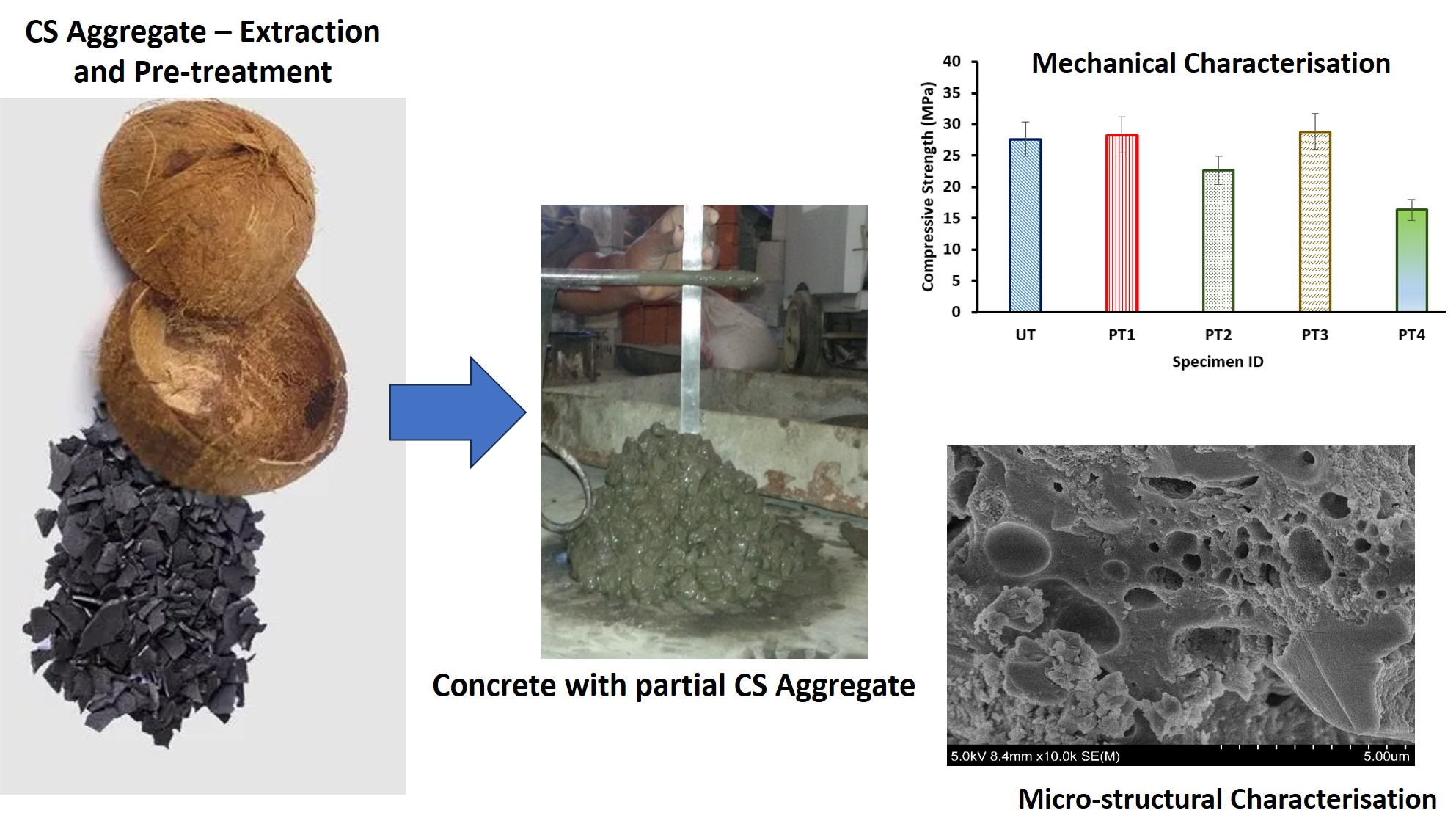
In this study, an attempt is made to understand the effectiveness on initial treatment of coconut shell on the strength of concrete. The coconut shell materials obtained from the agricultural wastes are used as a replacement for coarse aggregate in conventional concrete. From the particle size distribution graph, the CS aggregates follow a similar trend of smooth grain distribution when compared to conventional aggregates. Coconut shell aggregates were treated using different method with the solutions of sodium silicate, calcium hydroxide, polyvinyl alcohol and with heat. Treated coconut shells were tested for water absorption and their resistance to crushing and impact. Water absorption of PVA treated aggregates was reduced from 17.7% to 4.0% portraying the effectiveness of pre-treatment procedure. Compared to the untreated coconut shell aggregates, the impact and crushing values of heat treated ones reduced by 75.8% and 87.8% respectively. Coconut shell concrete specimens were tested for 28-day compressive strength, split tensile strength and flexural strength. The results of treated coconut shell concrete were compared with untreated coconut shell concrete. Compressive and split tensile strengths of CS concrete also increased with heat treatment whereas the flexural strength improved due to the calcium hydroxide treated aggregates. Micro-structural characterisation using Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) analysis showed the presence of strong interface between the aggregate particles and concrete.