- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 9 Downloads
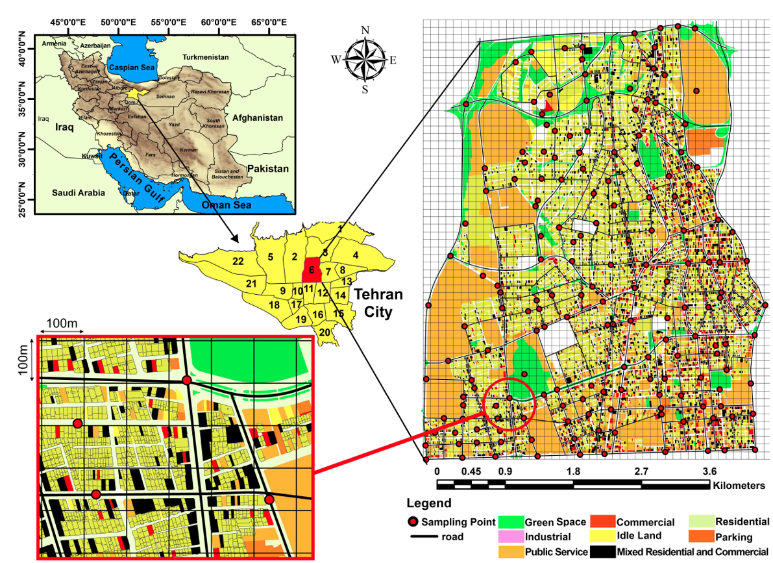
We utilized satellite and GIS technologies to address the relationship between urban land uses and Noise Pollution (NP) in one of the most crowded regions of Tehran city. Leq was determined in 170 stations of the studied area and an acoustic map was created. Moreover, using satellite remote sensing data and a land use map, the density map for nine types of the most important urban land use was provided and the relationship between different land use densities and NP was investigated. We found that the investigated region was highly polluted and the NP level was higher in the morning (76.29±5.61 dB[A]) and afternoon (76.46±4.88 dB[A]) in comparison to the noon period. Furthermore, the prepared acoustic map revealed that in the east and southwest of the studied area, the NP was highest and lowest, respectively. Also, cultural (73.48±4.7 dB[A]) and parking (79.02±4.3 dB[A]) areas had the lowest and highest levels of Leq. Also, the high density of road, commercial, industrial, mixed commercial and residential and parking land uses had a direct significant relationship with Leq and this relation was inverse for green space. It was concluded that land use variations significantly affect the NP levels and it can be utilized to predict and manage the NP in different cities.