- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 3 Downloads
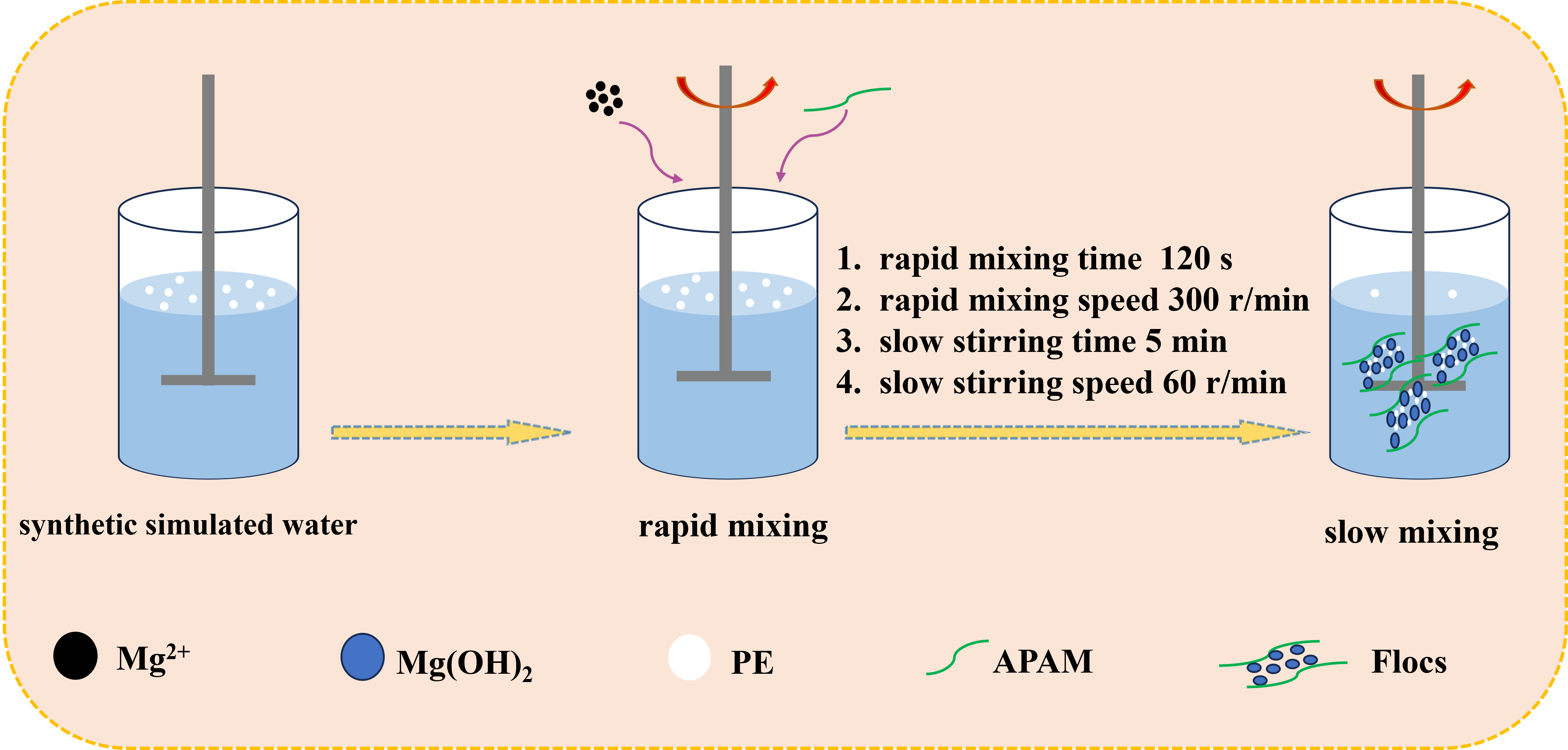
The effect of mixing conditions on coagulation-flocculation performance and floc characteristics was researched by treating simulated water containing polyethylene with magnesium hydroxide and anionic polyacrylamide as dual-coagulant under alkaline conditions. The floc size distribution and flocculation index were used as the indicators to investigate the floc formation conditions, aiming to discover the relationship between the flocculation effect and floc formation process. The images of flocs were in situ captured using a digital photomicrography to further the knowledge of flocs characteristics, such as floc morphology and settleability. In addition, a single variable was controlled to investigate the effect of different stirring conditions on the experiments by choosing stirring time and stirring speed. The results indicated that under the experimental conditions of rapid mixing for 120 s at 300 r/min or G value of 161.5 s-1, slow mixing for 5 min at 60 r/min or G value of 18.5 s-1, the removal efficiency of polyethylene-contaminated water was more than 84.9% ± 3% (mean ± SD, n = 3 ). According to the experimental results and coagulation performance of this system, the optimum conditions play an important role in floc growth and PE removal. Furthermore, this work was promising to supply useful recommendations on optimizing coagulation and flocculation.