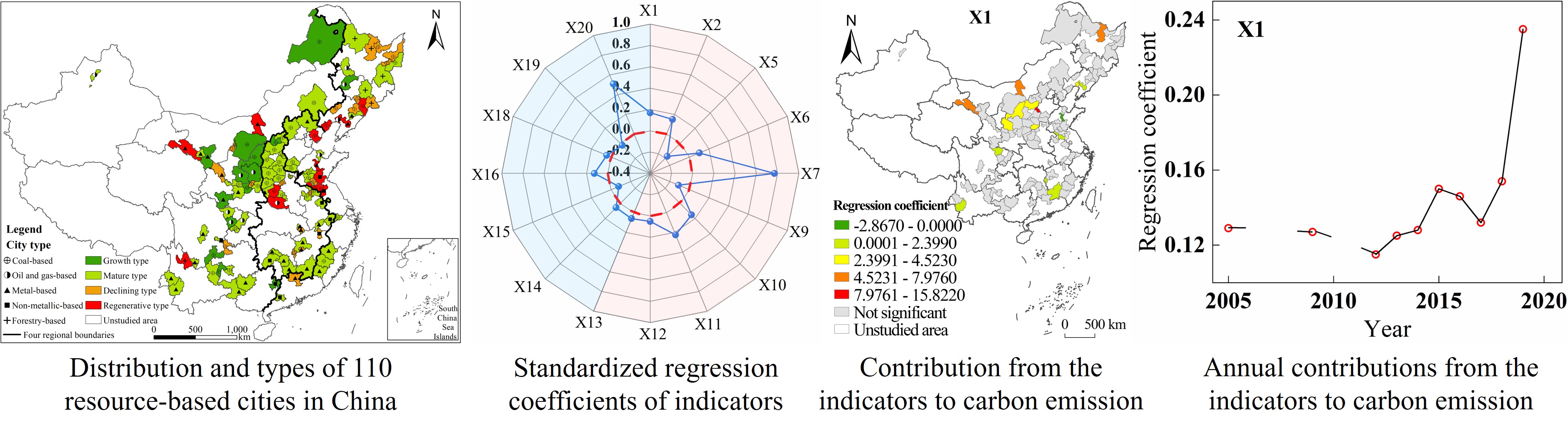
Resource-based cities are an important source area of carbon emissions in China. Urban carbon emissions are significantly affected by territorial space development and protection (TSDP). Based on the panel data of 110 resource-based cities in China from 2005 to 2020, an empirical model is constructed. The heterogeneous impacts of TSDP on carbon emissions are explored at multiple levels and angles, key influencing factors are identified, and carbon emission reduction strategies and differentiated low-carbon development paths are proposed. The results of the study: (1) On the global scale, the degree of explanation of TSDP on the carbon emissions of the overall cities reaches 76.2%, in which the GDP, energy consumption per unit of GDP and the proportion of tertiary industry make the greatest positive contribution. (2) At the local scale, the impact of TSDP is heterogeneous by type. GDP has no significant influence on economically backward cities, and the total population has the strongest positive contribution to less populated cities. (3) At the urban scale, the impact of TSDP has spatial heterogeneity. Economic development has the greatest influence on carbon emissions, while population aggregation has the opposite effect. GDP and energy consumption per unit of GDP are no longer the dominant factors in all cities. (4) The impact of TSDP is time-differentiated. During the study period, GDP and energy consumption per unit of GDP significantly and positively affect carbon emissions, and their contributions show “W”-shaped and “U”-shaped fluctuation changes respectively. The proportion of construction land area significantly and positively affects carbon emissions in 10 years, and the effect increases with time. The research results can provide theoretical support and decision-making reference for resource-based cities to realize low-carbon sustainable development.
Total file downloads: 11