- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 2 Downloads
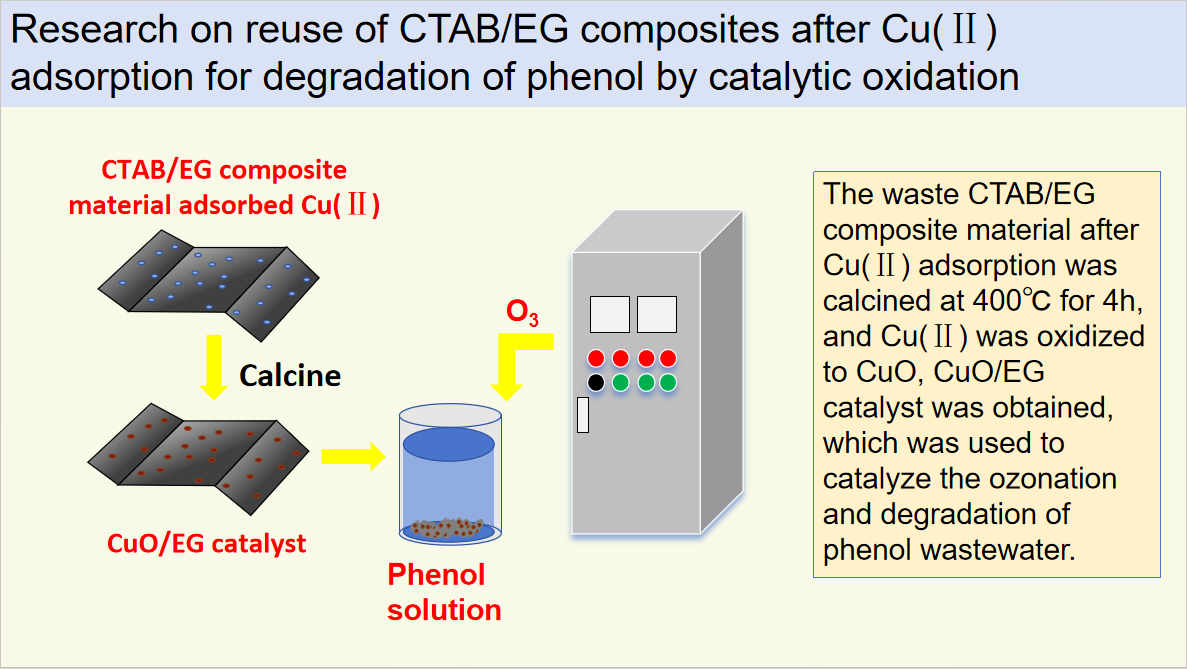
A copper oxide (CuO)/ expanded graphite (EG) catalyst was prepared, characterized and used to catalyze ozonation process to improve the degradation of phenol wastewater. The morphology of CuO/EG catalyst, the types of functional groups and the structure of crystal surface were analyzed by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and electron energy spectrum. To investigate its catalytic effect on phenol wastewater degradation by ozone. The key factors such as initial concentration of phenol, initial pH of solution and O3 concentration were investigated. When the initial concentration of solution is 500 mg/L, the optimal initial pH value of solution is about 6, when the dosage of catalyst is 1.2 g/L and the concentration of ozone is 1.8 mg/L, the removal rate of phenol is 91.2% after 30 min reaction, which is more efficient and rapid than the single ozone degradation system. After 5 reactions, the removal rate of phenol reached about 92.0%, indicating that the catalyst had good stability and reusability. The results show that CuO/EG material can be used as an important reusable resource for catalytic oxidation in the treatment of phenol wastewater.