- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 5 Downloads
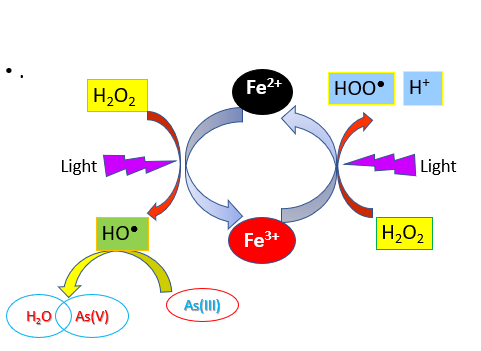
In this paper, photo-Fenton method has been systematically examined to oxidize the toxic and mobile As(III) in the solution by •OH radicals resulted from the reactions between Fe2+ and H2O2 under UV light, to form the less toxic and insoluble As(V). The effects of various experimental parameters including initial Fe2+ and H2O2 concentrations, working pH, and contact time were studied through a batch experiment. The concentration of As(V) resulted from the photo-oxidation was determined by visible spectrophotometry method based on the formation of arsenate molybdate solution. The results of the research attributed noticeably that the As(III) could be oxidized through photo-Fenton process to form As(V) that was assigned by a considerable decline in the concentration. The maximal oxidation of As(III) with 10 mg L-1 of the concentration in 50 mL of the aqueous solution, that was about 85%, can be reached in the presence of Fe2+ 10-2 mole L-1, H2O2 5. 10-2 mole L-1 at the working pH 3 and within 3 h of the reaction time. It has been also detected that for reaching the permissible level (lower than 0.01 mg L-1 ), three stages of the photo-Fenton process were required.