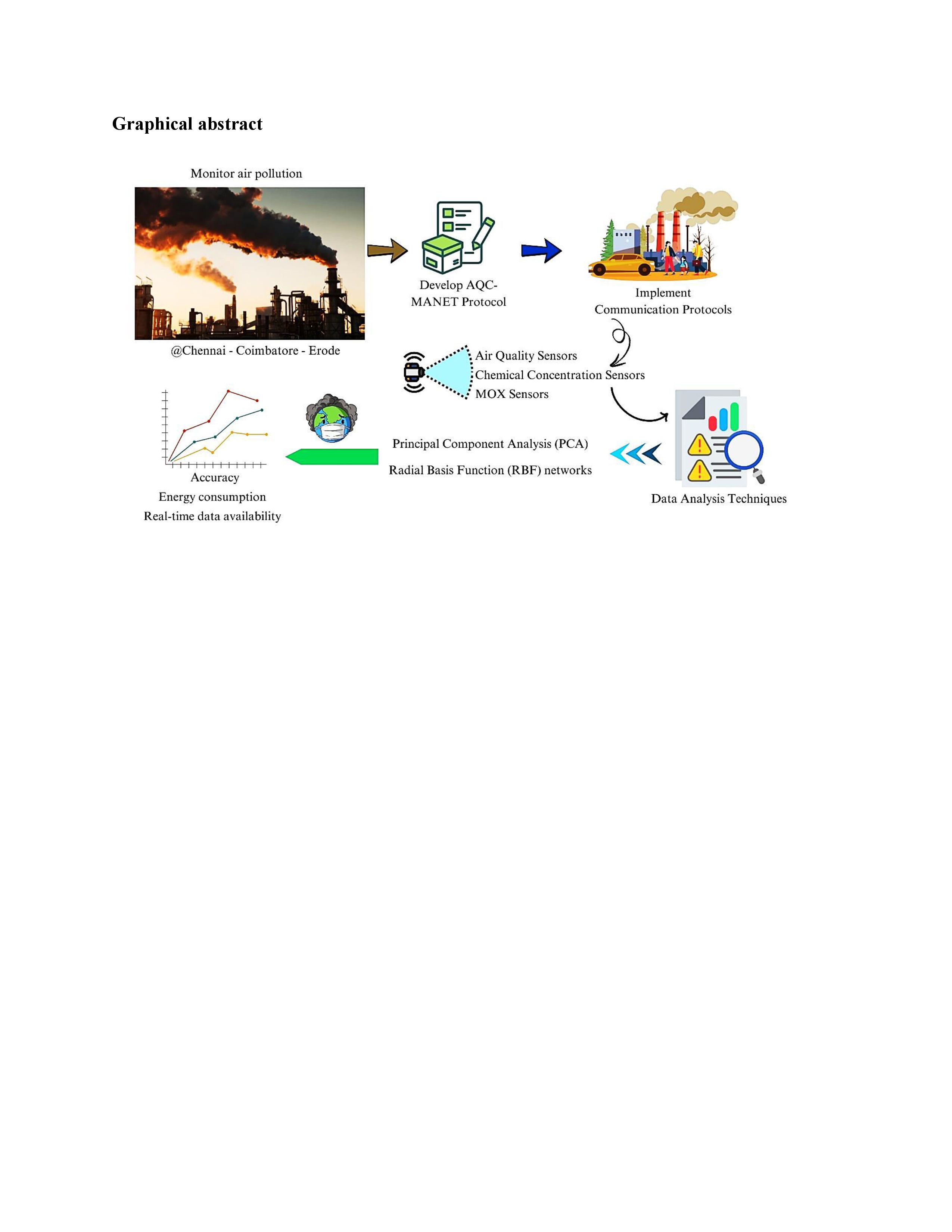
Air quality monitoring is becoming an increasingly important aspect of monitoring pollution due to changing environmental patterns in urban and industrial areas. This study designs an energy-efficient air quality monitoring system using Air Quality Clustering for Mobile Ad Hoc Sensor Networks protocol. The proposed system integrated Wireless Sensor Networks with Mobile Ad Hoc Networks addresses all the challenges related to data aggregation and routing within dynamic networks. Thus far, advanced air quality, chemical concentration, and MOX sensors have been used in Tamil Nadu cities such as Chennai, Coimbatore, and Erode, to monitor pollutants such as carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and particulate matter. The data will be transferred in real time to a cloud platform for analysis through ZigBee-based communication-supported by a database management system and an expert decision support system, and will act on the findings. Solar panel integration and advanced power management improvements yield 30% less energy consumption while assuring uninterrupted operation. The proposed protocol has improved cluster performance and decreased inter-cluster delays while extending the lifetime of the network to 320 hours. Comparisons of various methods show that the proposed method clearly outperforms conventional networks, achieving 92% pollutant classification accuracy, extending network lifetime to 320 hours, and ensuring continued communication with a very low packet loss rate of just 1%. The system transmits data in 6 seconds and provides results within 3.5 seconds, making it reliable and speed-efficient. Further, it achieves 150 Mbps throughput with a latency of only 25 ms. The system is also scaleable and offers real-time SMS alerts on localized monitoring, thus helping industries and other stakeholders in pollution management. Proposed methods may thus be revolutionary in air quality monitoring, providing energy-efficient real-time solutions in urban and industrial environments.
Total file downloads: 9