- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 2 Downloads
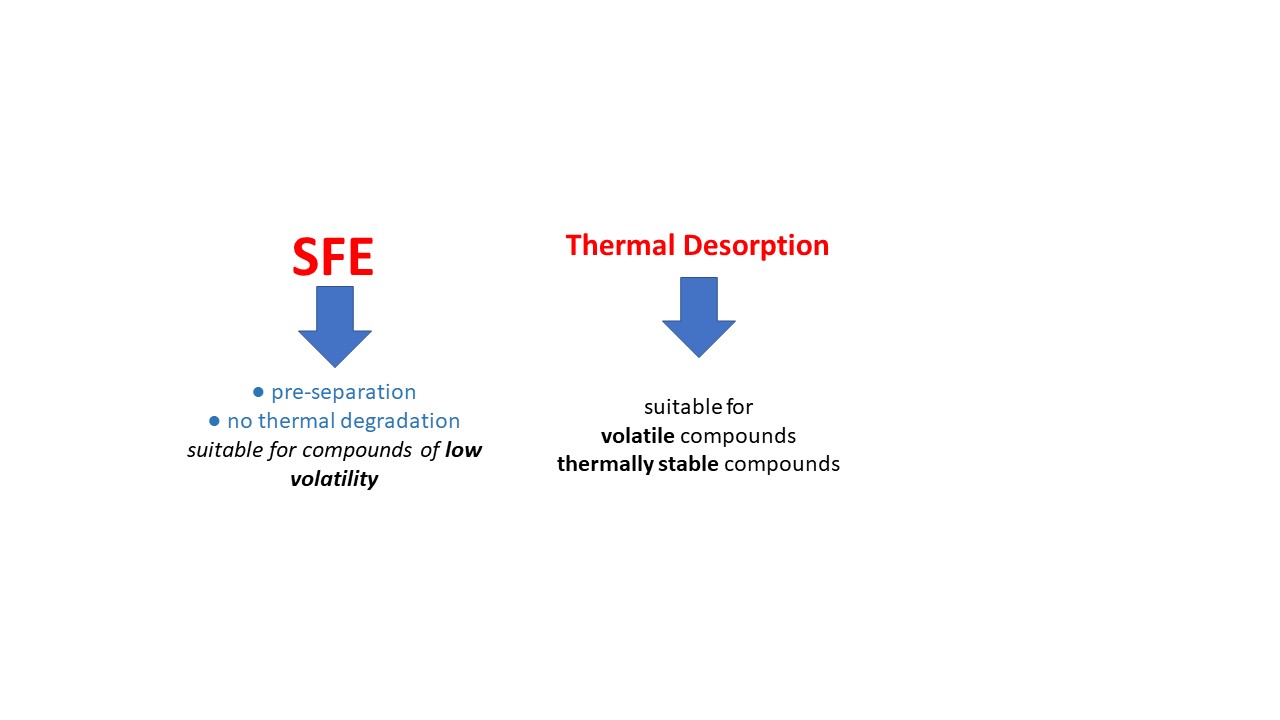
This study has been focused on the comparison of the application of Thermal Desorption (TD) and Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE) methods for the identification and quantification of organic chemicals in house dust samples. To investigate how the results obtained by SFE and TD of house dust compare to one another and whether the SFE has advantages over the TD method, an aliquot of a house dust sample has been subjected to desorption at successively increasing temperatures. The thermal desorption unit used cryo - focusing on capillary tubing and was connected to a GC-MS combination. A quantity of the same house dust sample was extracted, using a method consisting of a two-step SFE with CO2 and CO2 + 5% of methanol, and GC-MS analysis of the eluates. The comparison of the results showed that the SFE method was superior to the TD for analysing indoor dust samples because of the pre-separation and the absence of thermal degradation, particularly for compounds of low volatility. However, TD could be more appropriate for relatively volatile or lower molecular weight range compounds and thermally stable compounds.