- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 27 Downloads
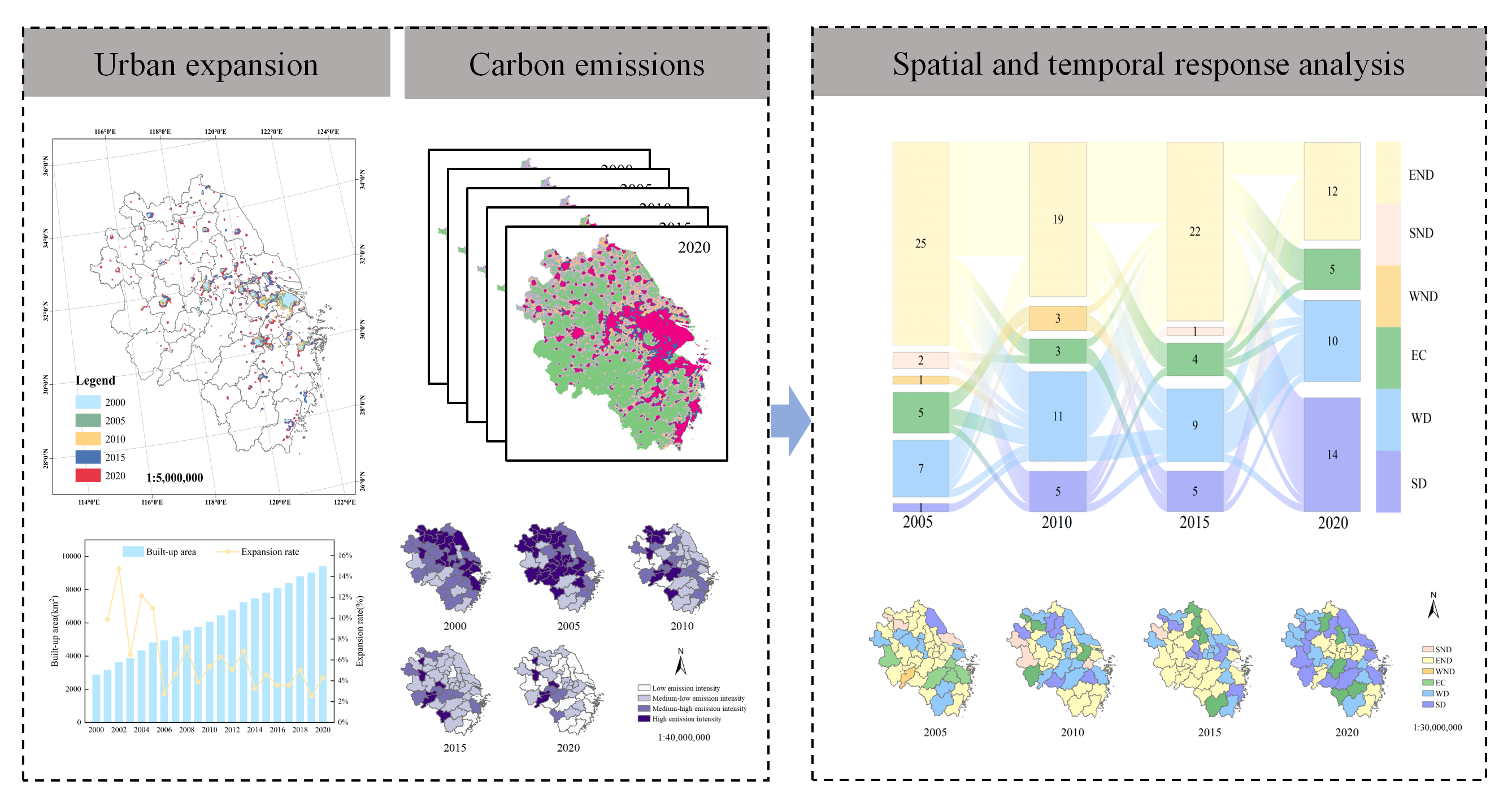
Dynamically understanding the spatial and temporal evolution of the relationship between carbon emissions and the process of urbanization. is of great significance for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting the high-quality development of the regional economy. In this paper, the characteristics of the urban expansion in China's Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration (YRDUA) from 2000 to 2020 are analyzed using nighttime light data, each city's carbon emission intensity is calculated by combining statistics on carbon emissions, and a quantitative study on the relationship between carbon emissions and urban expansion is conducted. The results of this study indicate that from 2000 to 2020, the built-up area in the YRDUA continued to expand. The expansion rate exhibited a fluctuating evolution pattern of increasing and decreasing and the carbon emission intensity decreased year after year, with a larger decrease from 2005 to 2010 compared with the other three periods. The urban expansion in the YRDUA promoted an increase in carbon emissions, but decoupling also occurred and transitioned from expansion of negative decoupling to weak decoupling and strong decoupling. By 2020, 70% of the cities in the YRDUA were in a state of decoupling.