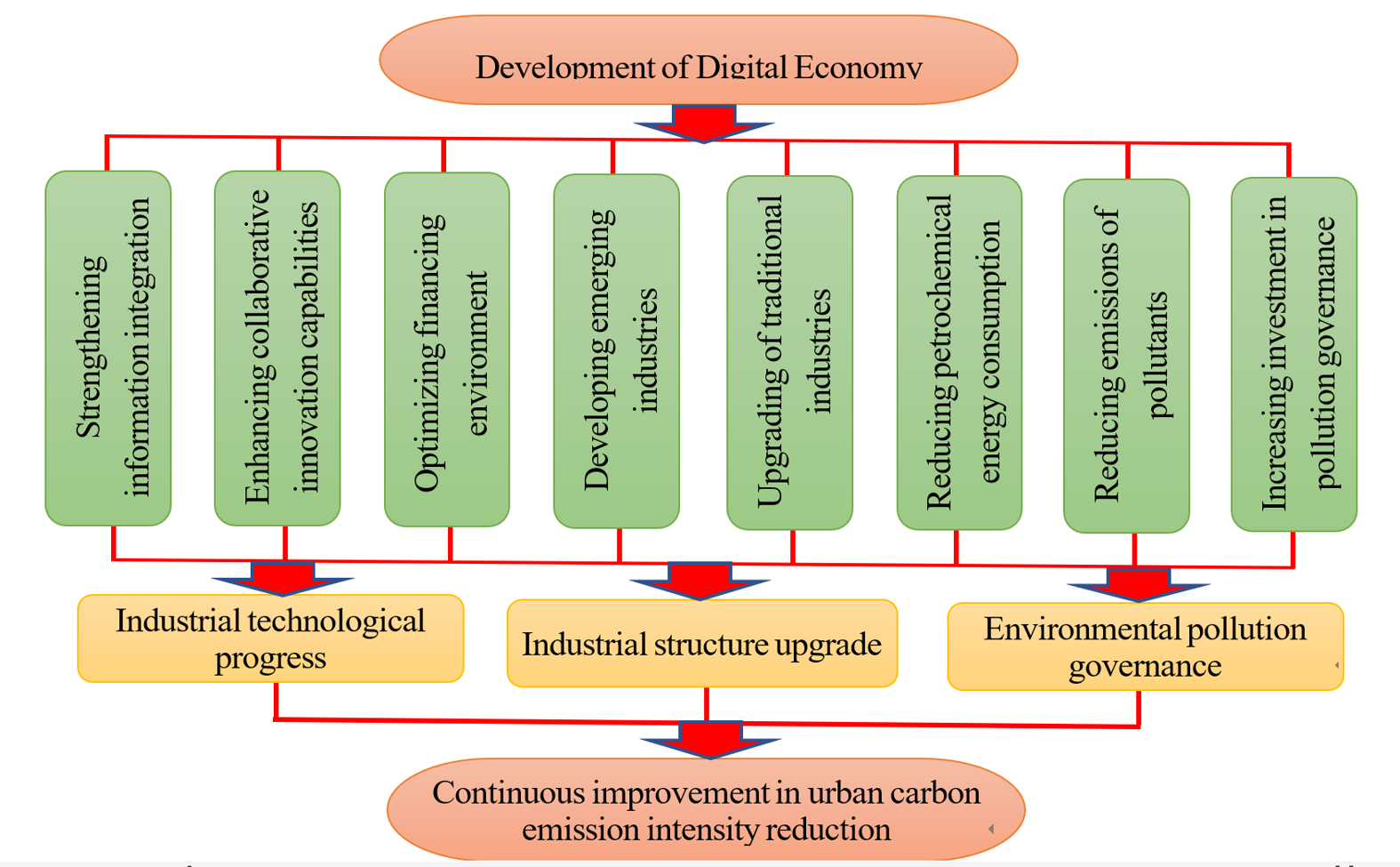
In order to explore the influence of digital economy development on carbon emission intensity from urban energy consumption, digital economy development is incorporated into the reduction framework of carbon emission intensity from urban energy consumption in this paper. With carbon emission intensity from urban energy consumption in China taken as the research object, empirical tests and dynamic effect analyses were carried out on the factors influencing carbon emission intensity from urban energy consumption, using urban panel data for the period of 2012–2022. It is found that digital economy has a significant inhibitory effect on carbon emission intensity from urban energy consumption in China, with a coefficient of -0.348. Among the five selected control variables, PCG, UR, and IS show a positive correlation with carbon emission intensity from urban energy consumption, enhancing EI with corresponding influence coefficients of 0.472, 0.135, and 0.331 respectively; EGRI and TRL show an inverse correlation with EI, inhibiting the growth of EI with corresponding influence coefficients of -0.556 and -0.201, respectively. Policy suggestions were put forward to minimize EI on the basis of the test results combined with the actual situation of China's urban economic development.
Total file downloads: 12