- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 8 Downloads
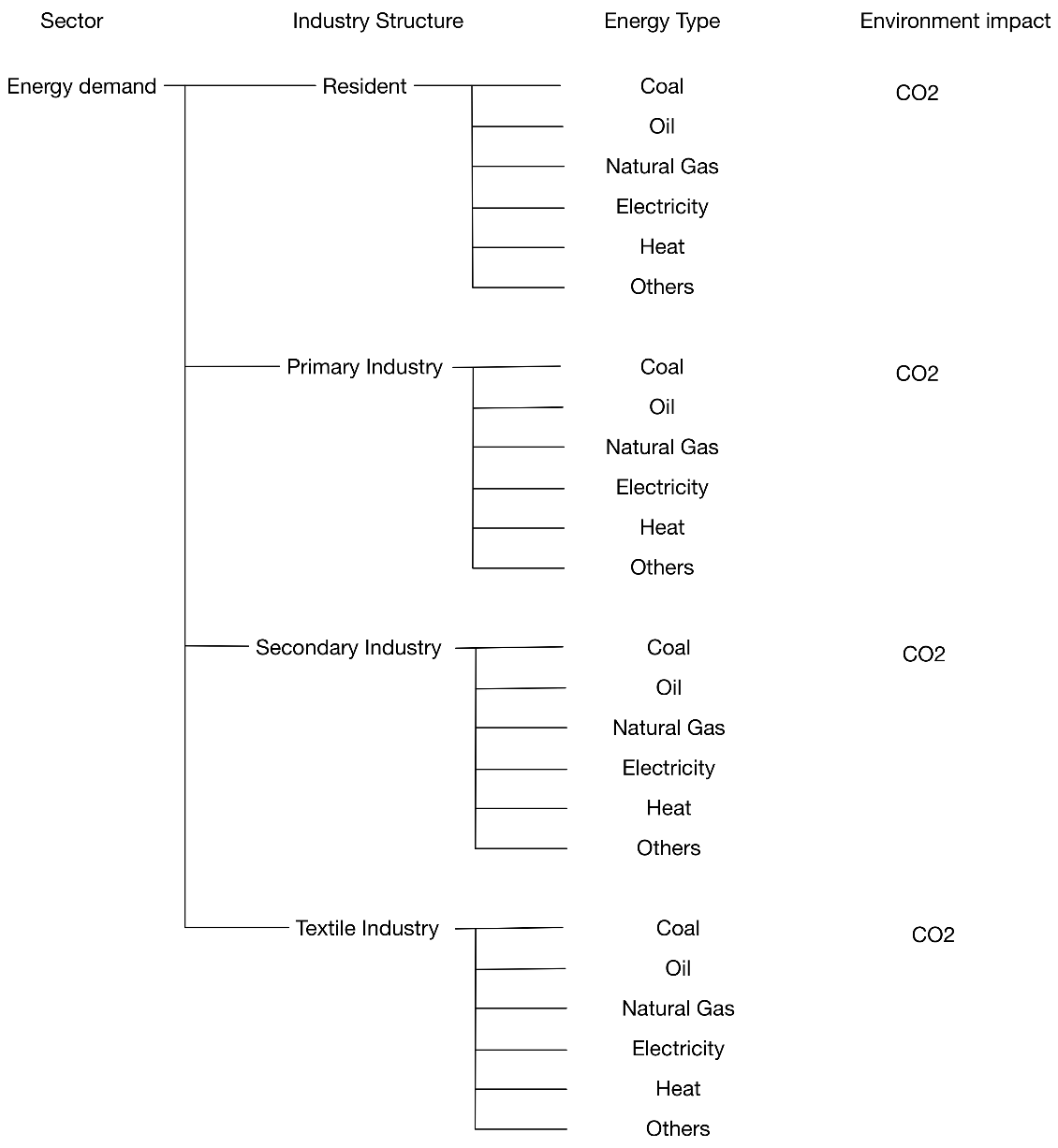
The long-term forecasting of the energy demand is an important issue of an area’s sustainable development, especially for mega cities such as Beijing. Beijing is changing its energy supply strategy to depend on energy imports from other provinces due to the city’s long-term low carbon sustainable development plan. Beijing has promised that it will reach the peak value of energy consumption by 2050 and the peak value of the carbon emissions by 2030. To understand whether this can be achieved, this study built an energy demand simulation model using the LEAP with different development scenarios. The results show that, the peak value of Beijing’s energy demand is between 108.25 and 131.74 Mtce during the period of 2044 to 2048, while the peak value of carbon emissions is between 134 and 139.38 million tons in 2025. We also find that adjusting the industry structure and improving the tertiary industry’s energy usage efficiency can be efficient ways to reduce energy consumption. These approaches not only reduce the negative influence of the economic development, but also achieve the energy saving and carbon emission reducing requirements. This study provides an interpretation of the implications for the future energy and climate policies of Beijing.