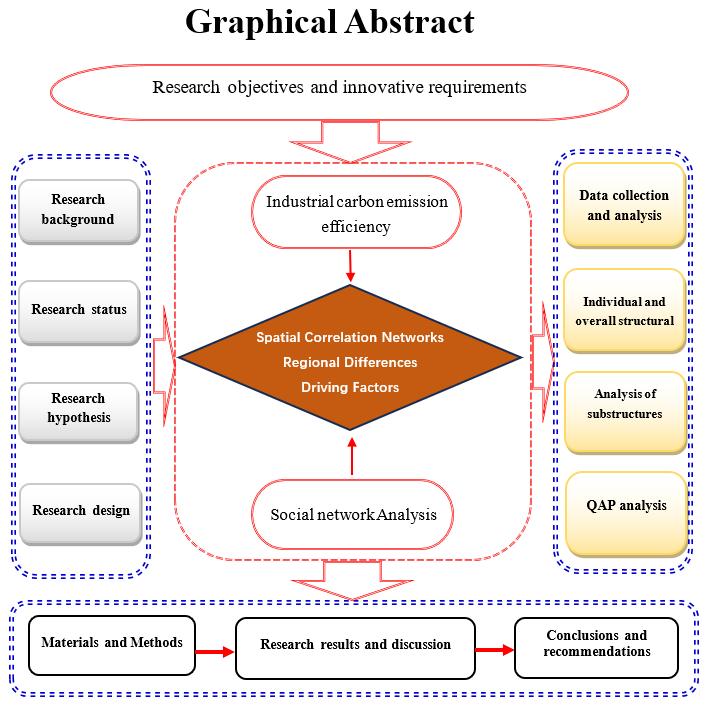
Abstract: Green and sustainable development of industry has gradually become an essential factor for economic development, effective improvement of industrial carbon emission efficiency (ICEE) has a contributing role in realizing industrial carbon emission reduction and sustainable economic development. According to this study, the spatial correlation characteristics and driving factors of ICEE in the Yangtze River Delta (YRD) urban agglomeration are analyzed by using social network analysis and the QAP model. Empirical results show that (1) the spatial variation of ICEE in YRD urban agglomeration is large, showing a decreasing trend from the southeastern cities to the northwestern cities. (2) The spatial correlation network presents a pattern of development from core cities to edge cities, with Suzhou, Changzhou, Hangzhou, etc. as the center to the south and west cities of YRD urban agglomeration. (3) The ICEE substructures in YRD urban agglomeration have four plates, namely "inflow plate", "outflow plate", "bidirectional outflow plate" and "agent plate". (4) The spatial correlation network of ICEE is significantly influenced by the matrix of differences in research and development capabilities, environmental regulation, and rate of foreign investment.
Total file downloads: 17