- Cite article
- Download PDF
- Share article
- 23 Downloads
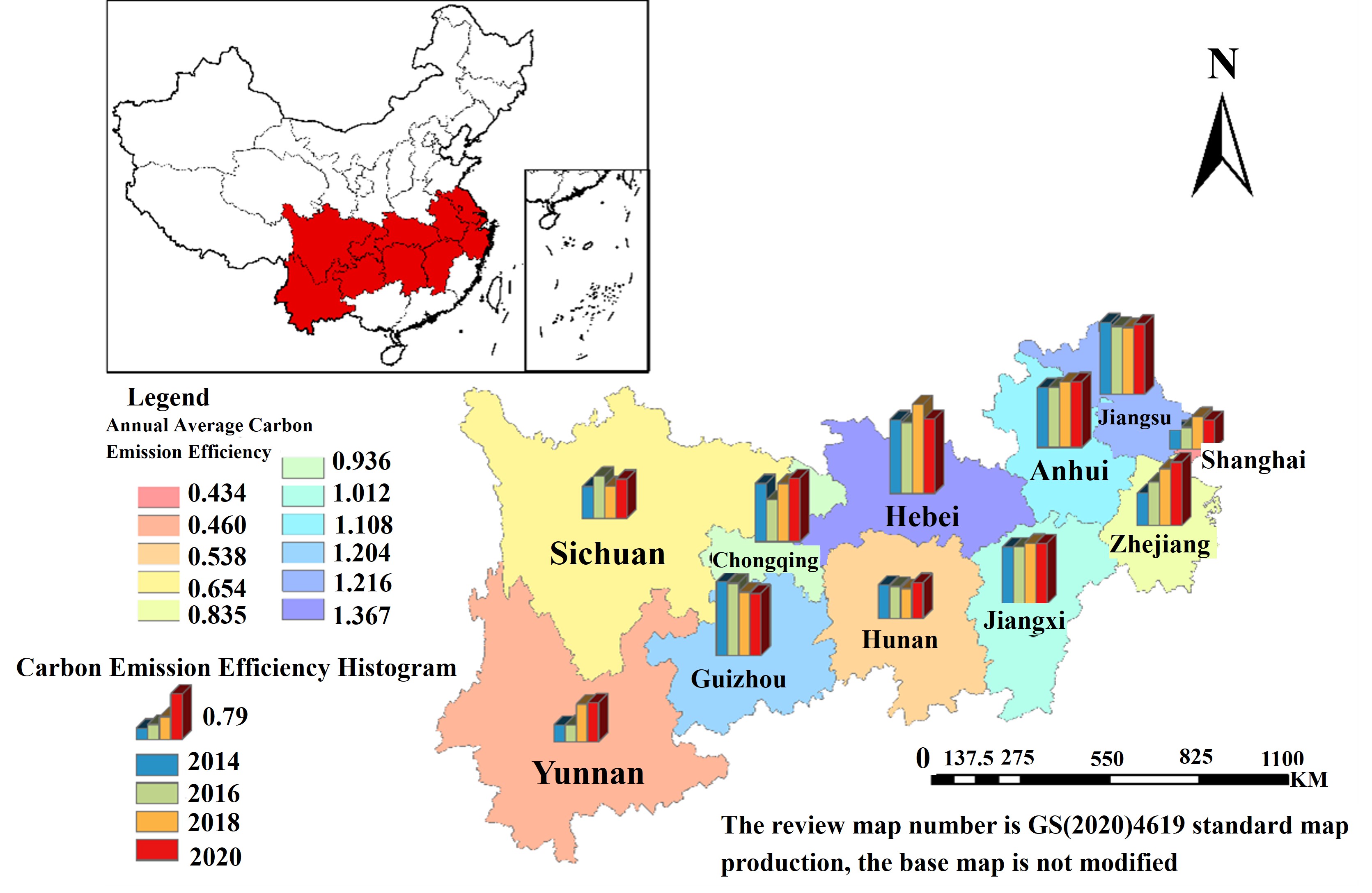
Severe climate problems have forced the Chinese government to put forward the goal of "carbon peak" and "carbon neutrality". The transport sector is a key area for carbon reduction. Based on this background, this paper constructs the Super-SBM model and the Malmquist-Luenberger index model containing the undesirable output. This paper measures the carbon emission efficiency of transport industry in China's Yangtze River Economic Belt from static and dynamic perspectives during 2014-2020. Finally, the GTWR model is constructed to analyze the factors affecting carbon emission efficiency. The results show that: (1) the carbon emission efficiency of provinces in the Yangtze River Economic Belt is characterized by heterogeneity. Hubei was the highest, while Shanghai, Hunan, Sichuan and Yunnan were below average. (2) According to the Malmquist-Luenberger index analysis, the transportation carbon emission efficiency of the Yangtze River Economic Belt has a downward trend. Over the 2014-2020 period, carbon efficiency will decline by an average of 7% per year. (3) Energy consumption structure, industrial upgrading, economic development and population agglomeration have significant effects on carbon emission efficiency.